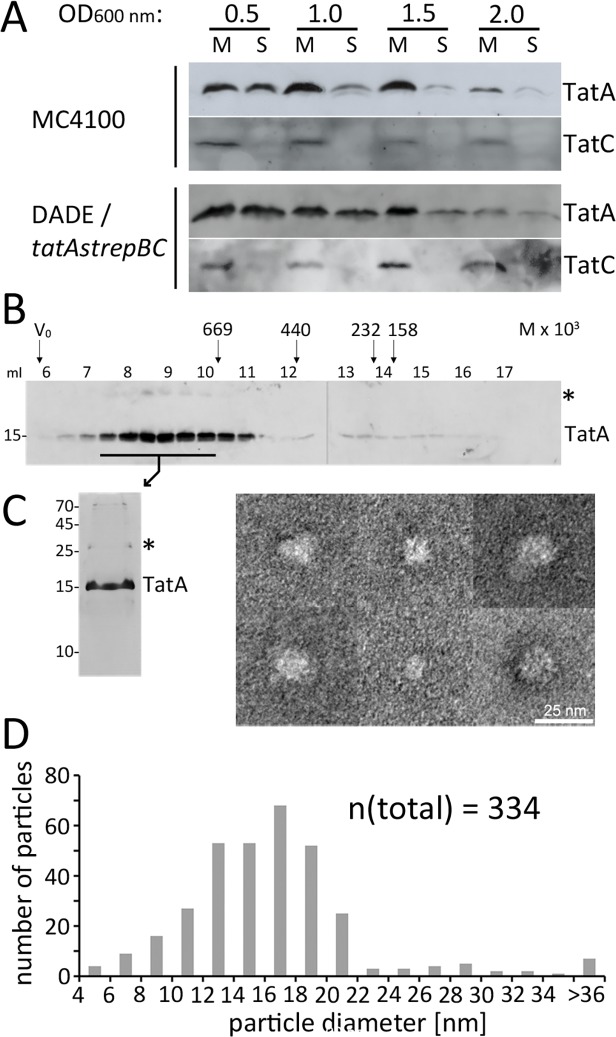
Fig 6. Membrane-detached soluble TatA forms large micellar associations.
(A) Soluble TatA is abundant after cell disruption of bacteria at early exponential growth phase. Distribution of TatA in the membrane and cytoplasmic fraction in preparations from cultures of strains MC4100 and DADE tatA-strep-tatBC, harvested at indicated optical densities. Fractionation control was done by detection of the polytopic membrane protein TatC. Samples were normalized to the same amount of cells. (B) Size exclusion chromatography (SEC) of TatA-strep as purified from the cytoplasm after wild-type level production (DADE tatA-strep-BC) indicates formation of high molecular weight complexes. Western blot analysis of elution fractions; SEC molecular weight markers are indicated at the top (thyroglobulin, 669 kDa; ferritin, 440 kDa; catalase, 232 kDa; aldolase, 158 kDa). (C) Silver-stained SDS-PAGE of purified TatA-strep and analysis of the TatA particles by electron microscopy. Six typical TatA assemblies are shown; see supplement S4 Fig. for an overview micrograph. (D) Statistical analysis of TatA particle diameters based on 334 measured particles. M, membrane fraction; S, soluble fraction; *, TatA dimer. Molecular weight marker positions (in kDa) are indicated on the left of SDS-PAGE blots.