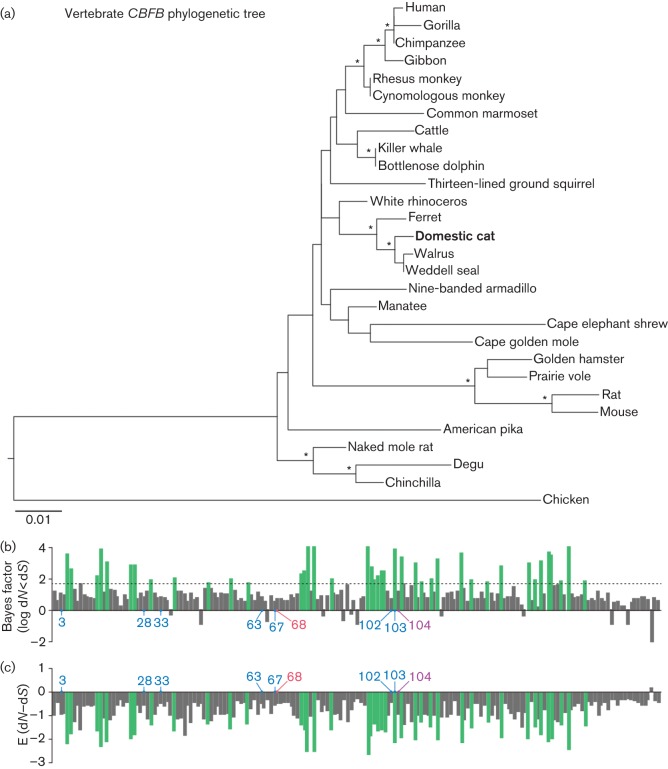
Fig. 1.
Molecular phylogenetic analyses of CBFB. (a) Phylogenetic tree of 29 CBFB genes reconstructed using the maximum-likelihood method. Chicken CBFB was used as an outgroup. Nodes with >70 % bootstrap values are indicated with asterisks. (b, c) Negative selection in 29 CBFB genes inferred by the REL method in HyPhy. The Bayes factor for dN<dS (negative selection) (b) and the E (dN–dS) value (c) are shown. RUNX1-binding sites (aa 3, 28, 33, 63, 67, 102 and 103; blue) (Bravo et al., 2001; Tahirov et al., 2001; Yan et al., 2004), Vif-binding site (aa 68; red) (Hultquist et al., 2012b), and the site binding to both RUNX1 and Vif (aa 104; purple) are indicated. The green bars represent the 41 negatively selected sites identified with Bayes factor >50. The dotted line in (b) indicates the Bayes factor threshold of 50 specified for the REL analysis.