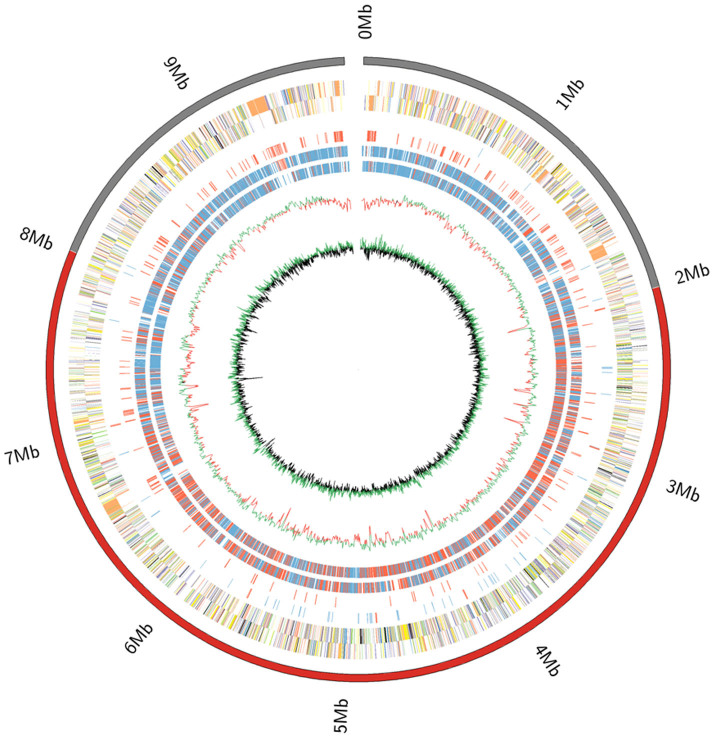
Figure 1. Circular representation of the S. albulus ZPM chromosome.
Circles 1 and 2, all genes (forward and reverse strands, respectively) are color-coded by function (blue, RNA processing and modification; vlblue, Chromatin structure and dynamics; chrm, Energy production and conversion; churn, Cell cycle control, cell division, chromosome partitioning; lgreen, Amino acid transport and metabolism; vlgreen, Nucleotide transport and metabolism; grey, Carbohydrate transport and metabolism; dblue, Coenzyme transport and metabolism; dyellow, Translation, ribosomal structure and biogenesis; vlred, Transcription; vlyellow, Replication, recombination and repair; lpurple, Cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis; black, Posttranslational modification, protein turnover, chaperones; vlorange, Inorganic ion transport and metabolism; lorange, Secondary metabolite biosynthesis, transport and catabolism; dpurple, General function prediction only; vlpurple, Function unknown; lred, Signal transduction mechanisms; dgrey, Intracellular trafficking, secretion, and vesicular transport; vvlgrey, Defense mechanisms); Circle 3, tRNA (red) and rRNA operon (blue); Circle 4, secondary metabolism genes; Circles 5 and 6 (forward and reverse strands), distributions of conserved (red) and strain-specific genes (blue) in the S. albulus ZpM genome compared with 11 other Streptomyces species; Circle 7, GC content; Circle 8, GC bias ([G − C/G + C], green indicates values > 1, dark < 1). The inside scale is numbered clockwise in Mb. The outer scale indicates the core (red) and noncore (gray) chromosomal regions. The origin of replication (Ori) is also indicated.