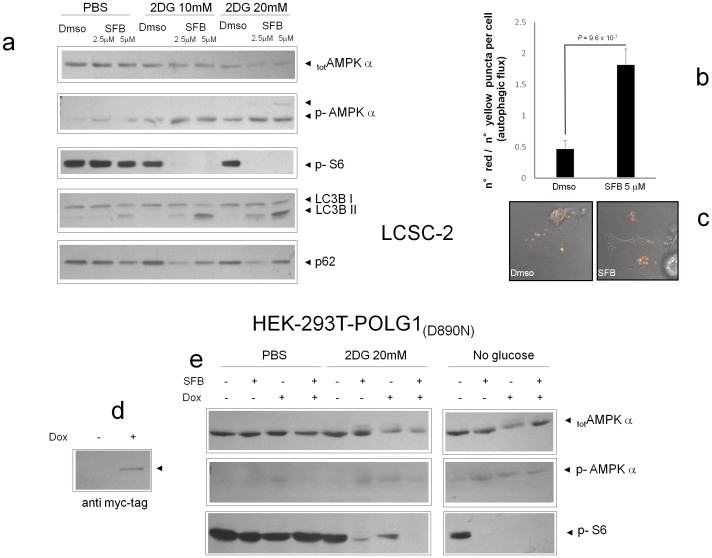
Figure 5. AMPK links metabolic damage by SFB to the mTOR/autophagy cascade.
(a). Western blot analysis of protein lysates from LCSC-2 stimulated for 4–6 hours with the indicated combinations of SFB and 2DG. Phosphorylation of AMP (Ser 172) and of the mTOR effector S6 (Ser 235/236) were monitored by phospho-specific antibodies. Total AMPK is also displayed. In the lowest two panels, appearance of a fast migrating LC3B band (LC3B II) and decreased anti-p62 signal in SFB and SFB + 2DG treated samples denote enhanced autophagy. Picture representative of three independent experiments with comparable results. (b). Confocal analysis of LCSC-2 cells transiently transfected with a tandem red-green flurescent tagged LC3 and exposed to SFB for 6 hours. Red puncta (autolysosomes) and yellow puncta (autophagosomes) were counted and the ratio calculated for each cell. a. Bars are mean ± SD of n = 51 (Dmso) and n = 32 (SFB); statistics by t-test. (c). representative fluorescent microphotographs displaying enhanced autophagic flux (prevalence of red over yellow dots) in the sample exposed to SFB. (d). Expression of myc-tagged POLG1 (D890N) in HEK293 cells ten days after cultivation in the presence of 50 ng/ml doxycyclin. (e). Induced (Dox+) and non induced (Dox−) HEK-293 POLG1 (D890N) cells were stimulated for 4 hours as indicated (SFB + = 5 μM) and phosphorylation of AMPK and S6 evaluated by immunoblotting as in a. Total AMPK is also depicted. In the latter panel, appearance of a faint slow migrating band above the main one confirms AMPK hyperphosphorylation. SFB has little effect on AMPK in this highly glycolytic cell line, unless glycolysis is inhibited (2DG and No Glucose). Mitochondria depletion cancels SFB stimulatory effect on AMPK.