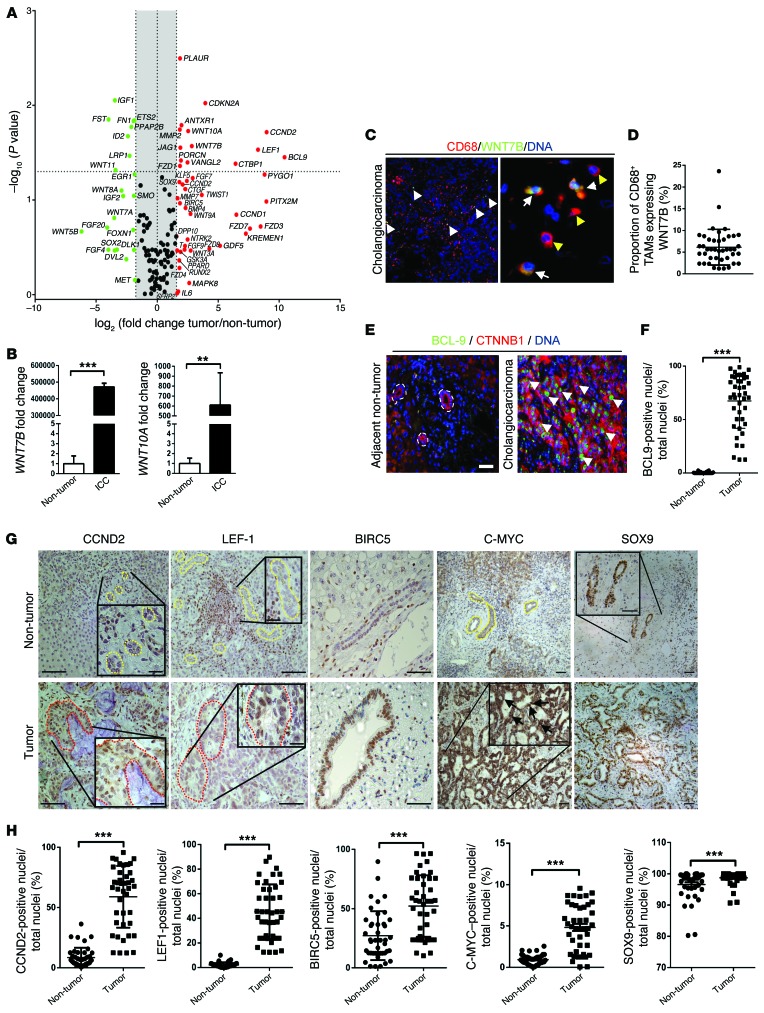
Figure 1. Canonical WNT signaling is activated in human CC.
(A) mRNA expression of WNT pathway genes and WNT target genes in CC versus patient-matched non-cancerous tissue (n = 11). Represented as a 3-fold change; P < 0.05. (B) WNT7B and WNT10A mRNA expression in human CC versus non-diseased liver (n = 37 vs. n = 30). (C) Immunohistochemistry of WNT7B (green) in CD68-positive macrophages (red). (D) Quantification of CD68+WNT7B+ TAMs (n = 42). (E) Immunohistochemistry for CTNNB1 (red) and BCL9 (green) in human CC and non-tumor, patient-matched liver. (F) Quantification of biliary nuclear staining for BCL9 (n = 42 per group). (G) Immunohistochemistry in non-tumor versus CC for CCND2, LEF1, BIRC5, C-MYC, and SOX9. Yellow lines, non-cancerous bile ducts; red lines, malignant biliary ducts; black arrows, nuclear positivity for C-MYC. (H) Quantification of biliary nuclear staining for CCND2, LEF1, BIRC5, C-MYC, and SOX9 in non-tumor and CC tissue (n = 42 per group). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Mann-Whitney U test; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Photomicrograph scale bars: 50 μm (in C, right panel, 20 μm).