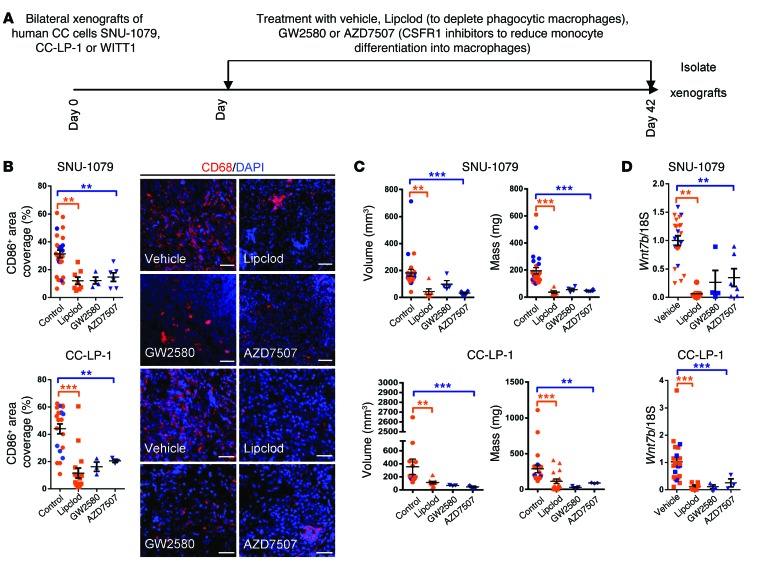
Figure 5. Macrophage ablation in human CC cell xenografts reduces tumor penetrance.
(A) Schematic demonstrating the strategy for macrophage depletion in human CC cell xenografts. (B) Quantification of CD68-positive macrophage number in SNU-1079 and CC-LP-1 xenografts following treatment with Lipclod, GW2580, or AZD7507 compared with vehicle alone. Photomicrographs: Immunohistochemistry in xenografts for CD68-positive macrophages (red). (C) Volume and mass of SNU-1079 and CC-LP-1 xenografts following treatment with Lipclod, GW2580, or AZD7507 compared with vehicle alone. (D) Murine Wnt7b expression in SNU-1079 and CC-LP-1 xenografts following treatment with Lipclod, GW2580, or AZD7507 compared with vehicle alone. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. A Kruskal-Wallis test was used to compare GW2580 and AZD7507 and control. Lipclod and control were compared using a Mann-Whitney U test in both cases. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Photomicrograph scale bars: 50 μm. For SNU-1079: PBS n = 11, liposomes n = 8, Lipclod n = 8, gavage vehicle n = 8, GW2580 n = 4, and AZD7507 n = 6. For CC-LP-1: PBS n = 9, liposomes n = 6, Lipclod n = 15, gavage vehicle n = 6, GW2580 n = 3, and AZD7507 n = 3.