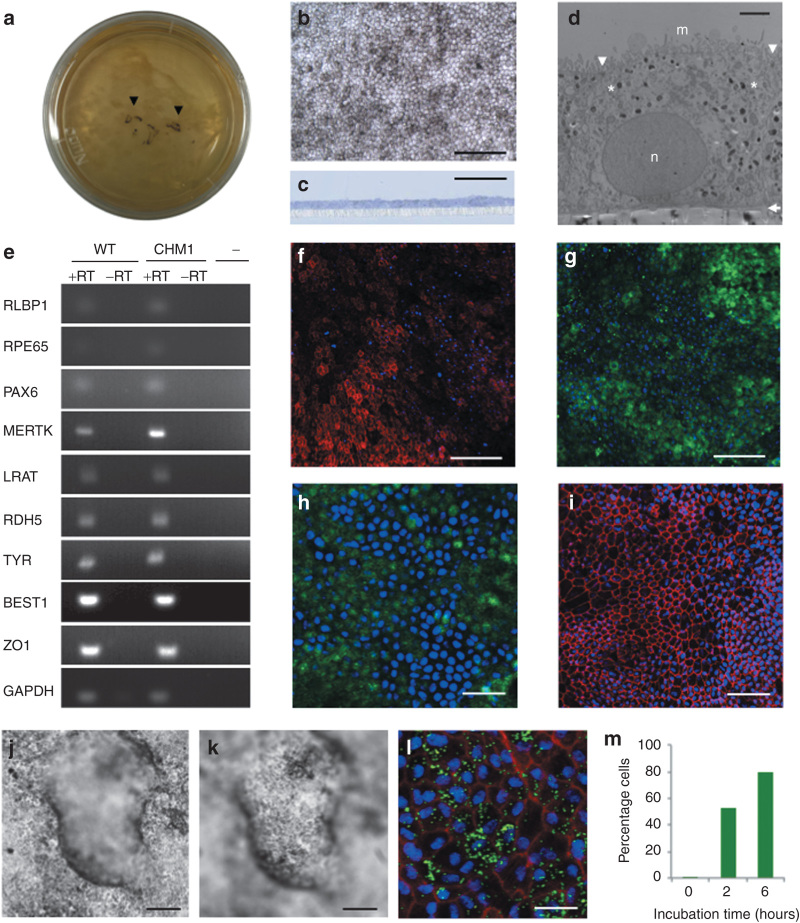
Figure 4.
Generation and characterization of iPSC-derived RPE. (a) Pigmented foci in confluent iPSC plates following bFGF depletion (arrowheads). (b) At confluence, passaged pigmented foci form a layer of polygonal pigmented cells. Bar = 100 µm. (c) Semi-thin section of iPSC-derived epithelium cultured on a porous filter and stained with toluidine blue demonstrates a regular monolayer (in blue) superposed on the filter (in white). Bar = 50 µm. (d) Transmission electron microscopy shows the iPSC-derived monolayer as a polarized epithelium with microvilli (m) on the apical side, desmosomes (arrowheads) at the apical junctions, melanosomes (asterisks) distributed throughout the cytosol, a nucleus (n) on the basal side, and a basal lamina (arrow) between the epithelium and the filter. Bar = 2 µm. (e) Expression of classic RPE genes, as determined by reverse transcriptase (RT)–polymerase chain reaction analysis in both wild-type (WT) and patient (CHM1) RPEs in the presence of RT (+RT). In the absence of RT (−RT) or complementary DNA (cDNA) (−), an amplicon was not detected. Immunofluorescence studies of the RPE monolayer, followed by confocal analysis, demonstrate the expression of (f) MERTK in the microvilli (in red), (g) CRALBP and (h) RPE65 in the cytoplasm (in green), and (i) ZO-1 at the apical junctions (in red). Bars = 100 µm (in f, g), 30 µm (in h), and 50 µm (in i). Apicobasal fluid transport causes the RPE to form fluid-filled domes, detaching it from the cell culture plate: (j) focus on the RPE adhered to the plate; (k) focus on the RPE at the top of the dome. Bars = 100 µm. (l) Confocal analysis of the RPE 6 hours postincubation with FluoSpheres showing the internalized beads (in green), nuclei (in blue), and F-actin (in red). Bar = 15 µm. (m) Flow cytometry analysis showing the percentage of RPE cells that internalized FluoSpheres over time. bFGF, basic fibroblast growth factor; BEST1, bestrophin 1; CRALPB, cellular retinaldehyde-binding protein; GAPDH, glycerglyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; iPSC, induced pluripotent stem cell; LRAT, lecithin retinol acyltransferase; MERTK , C-mer proto-oncogene tyrosine kinase; PAX6 , paired box 6; RDH, retinal dehydrogenase 5; RLBP1, retinaldehyde binding protein 1; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; TYR, tyrosinase; ZO1, zona occludens protein 1.