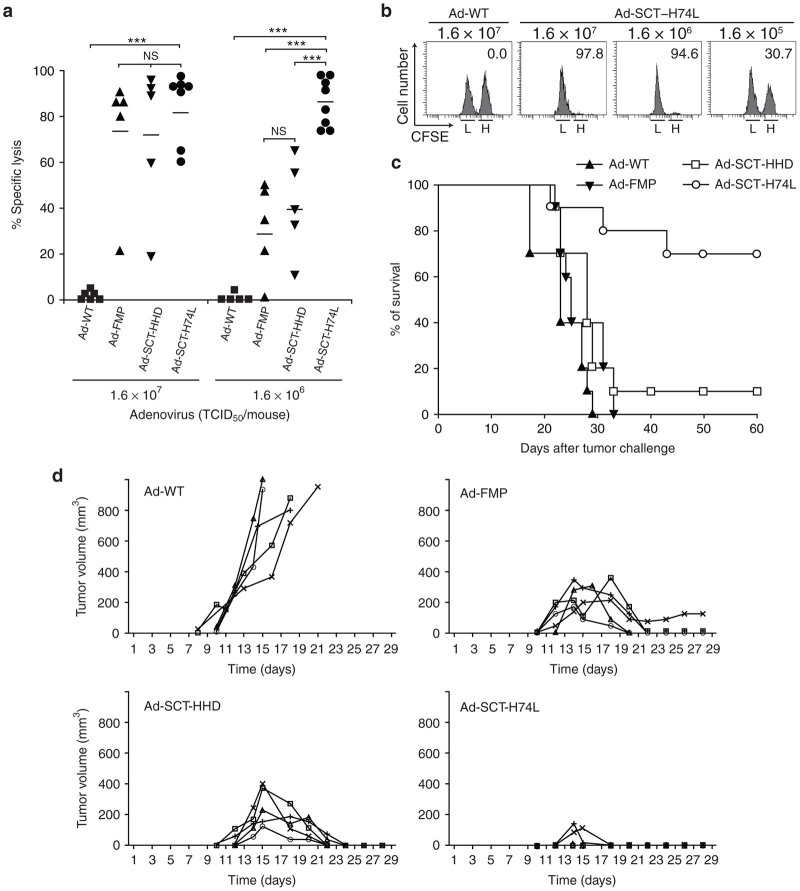
Figure 6.
Immunization with Ad-SCT-H74L induces strong antitumor protection in HHD mice. (a,b) In vivo cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) assay with tumor cells. Mice (five to eight per group) were vaccinated with Ad-WT, Ad-FMP, Ad-SCT-HHD or Ad-SCT-H74L at various doses. One week later, RMA-HHD and RMA-HHD-FMP cells were labeled with 0.25 and 2.5 μmol/l of CFSE, respectively, mixed at 1:1, and injected i.v. into each mouse (1 × 107 cells per mouse). After 12–14 hours, spleen cells were prepared and stained with PE-conjugated anti-H-2Db mAb. After washing, H-2Db+ cells were analyzed for their expression of CFSE by flow cytometry. (a) Each symbol represents an individual mouse. Horizontal bars represent the mean. ***P < 0.001; NS, not significant, One-way analysis of variance. (b) Representative data of the in vivo CTL assay are shown. The numbers in the panels indicate the percentage of FMP-specific lysis. L: RMA-HHD labeled with 0.25 μmol/l CFSE; H: RMA-HHD-FMP labeled with 2.5 μmol/l CFSE. (c) Survival of mice. After 1 week following immunization with 1.6 × 106 TCID50 of either Ad-WT, Ad-FMP, Ad-SCT-HHD or Ad-SCT-H74L, mice (ten per group) were challenged i.v. with 5 × 106 RMA-HHD-FMP cells. The experiment was repeated twice with similar results. (d) Inhibition of tumor growth. Mice (five per group) were immunized with 1.6 × 106 TCID50 of Ad-WT, Ad-FMP, Ad-SCT-HHD or Ad-SCT-H74L. After 1 week, mice were challenged subcutaneously with 5 × 104 RMA-HHD-FMP cells/mouse and monitored for the tumor growth. Curves represent individual mice. The experiment was repeated twice with similar results.