Figure 2.
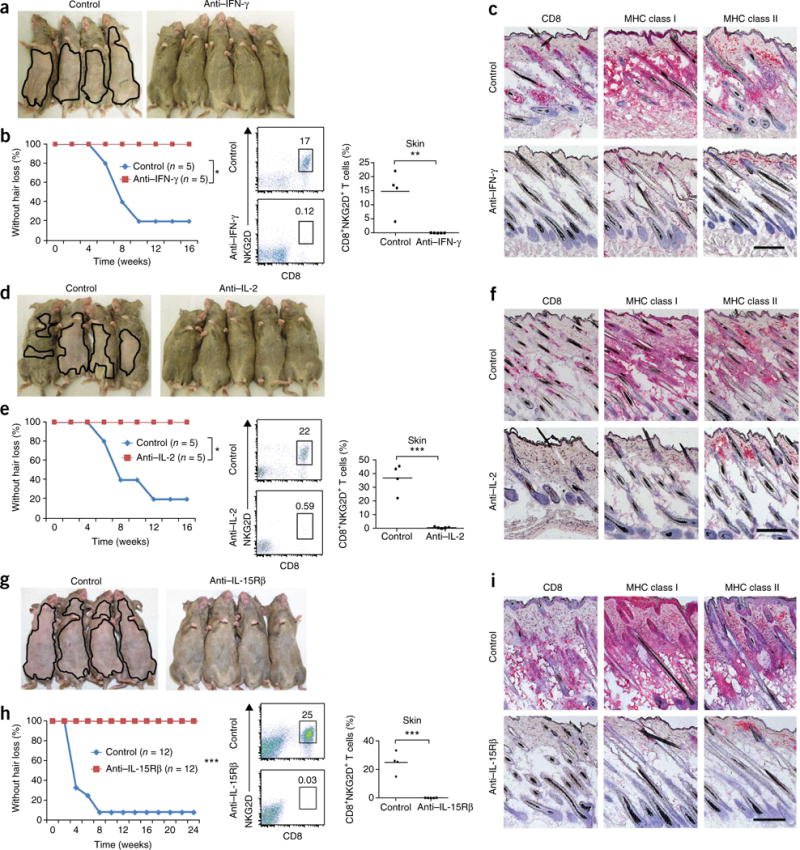
Prevention of AA by blocking antibodies to IFN-γ, IL-2 or IL-15Rβ. C3H/HeJ grafted mice were treated systemically from the time of grafting. (a–h) AA development in C3H/HeJ grafted mice treated systemically from the time of grafting with antibodies to IFN-γ (a,b), IL-2 (d,e) and IL-15Rβ (g,h). Frequency (number shown above boxed area) of CD8+NKG2D+ T cells in the skin of mice treated with antibodies to IFN-γ (b), IL-2 (e) and IL-15Rβ (h) compared to PBS-treated mice. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, statistical methods described in the Supplementary Methods. Immunohistochemica staining of skin biopsies showing CD8 and MHC class I and II expression in skin of mice treated with isotype control antibody or with antibodies to IFN-γ (c), IL-2 (f) or IL-15Rβ (i). Scale bars, 100 μm. For each experiment, n and number of repeats are detailed in the Supplementary Methods.
