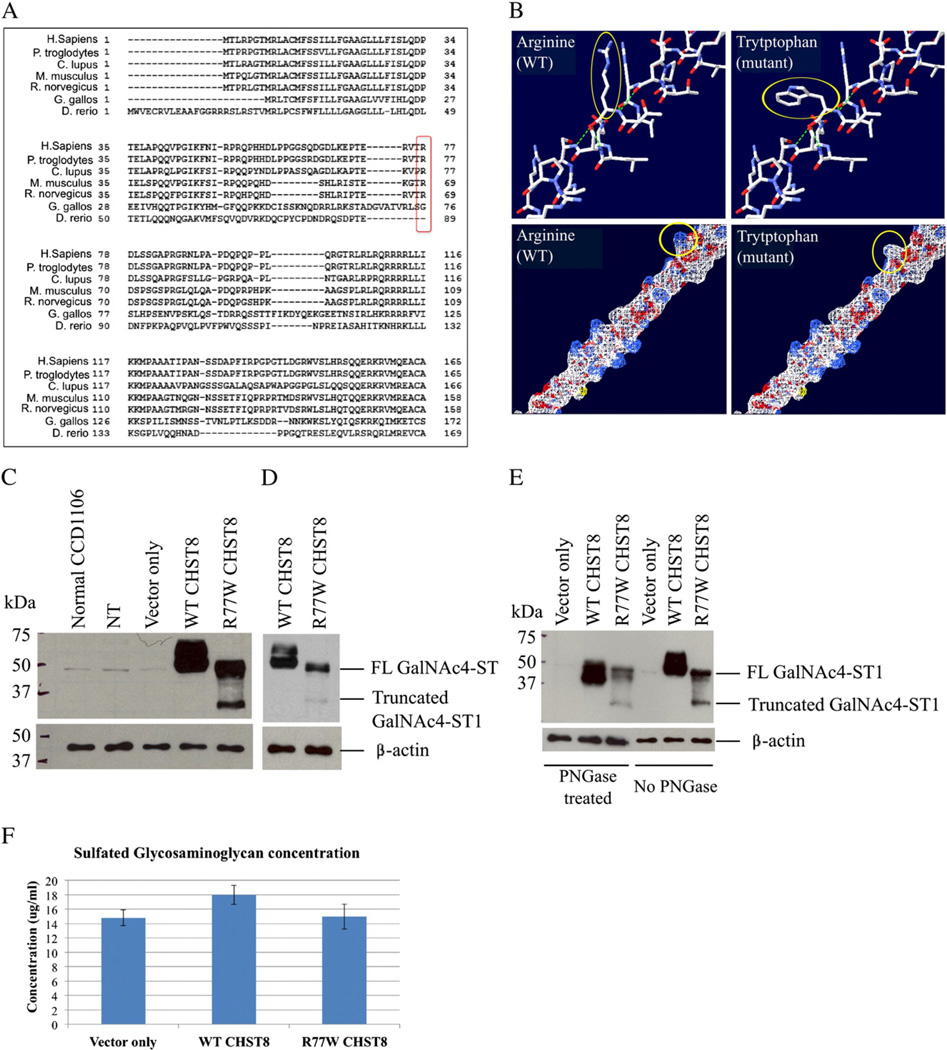
Fig. 3.
The c.229C>T (R77W) missense mutation results in decreased expression levels of full-length protein, loss of protein glycosylation and decreased activity of GalNAc4-ST1. (A) GalNAc4-ST1 protein sequence alignment across species (using HomoloGene, NCBI) shows that R77 is conserved among human, chimpanzee, dog, mouse and rat mammal species, but not in chicken or zebra fish. (B) Amino acid structure and electrostatic potential of GalNAc4-ST1 shows that the mutation perturbs amino acid hydrophilicity. Top panel: arginine (wild type) and tryptophan (mutant) amino acids are indicated with a red arrow. Blue = N, red = O, white = C, Bottom panel: a change in hydrophilicity due to the substitution of the basic amino acid arginine (white) by the non-polar amino acid tryptophan (blue) is indicated by the red arrow. Blue = basic amino acid, gray = non-polar amino acid. Figure generated using the Swiss-PdbViewer 4.0 application of the ExPASy Bioinformatics Resource Portal. (C and D) Western blot of whole cell lysates from CCD1106 keratinocytes transfected with c.229C>T mutant CHST8-pCMVscript (R77W CHST8) shows reduced levels of full length GalNAc4-ST1 (~49 kDa) compared to cells transfected with wild type CHST8-pCMVscript (WT CHST8). In addition, a lower molecular weight band (~35 kDa) is observed in whole lysates from cells overexpressing mutant CHST8, which is not detected in cells expressing wild type CHST8 and suggests increased degradation of mutant proteins. Normal keratinocytes (normal CCD1106), non-transfected keratinocytes that were incubated with Fugene HD only (NT) and cells transfected with empty pCMVscript (vector only) show low levels of full length GalNAc4-ST1. β-actin was used as a control of equal loading. FL = full length. (D) Lower exposure of blot B clearly showing lower levels of full length GalNAc4-ST1 in cells expressing mutant construct compared to wild type. (E) Western blot of wild type and mutant recombinant GalNAc4-ST1 proteins before and after treatment with PNGase reveals that, in contrast with wild type proteins, the mutant proteins are not subject to glycosylation. After PNGase treatment, WT proteins have smaller molecular weight than the untreated ones, but mutant proteins have identical molecular weights before and after treatment. (F) Colorimetric assay for total sulfated GAG quantification and comparison between cells transfected with wild type and mutant CHST8 constructs. Decreased levels of total sulfated GAGs are observed in cells expressing mutant GalNAc4-ST1 compared to wild type (n = 6), suggesting loss of function of mutant GalNAc4-ST1 proteins.