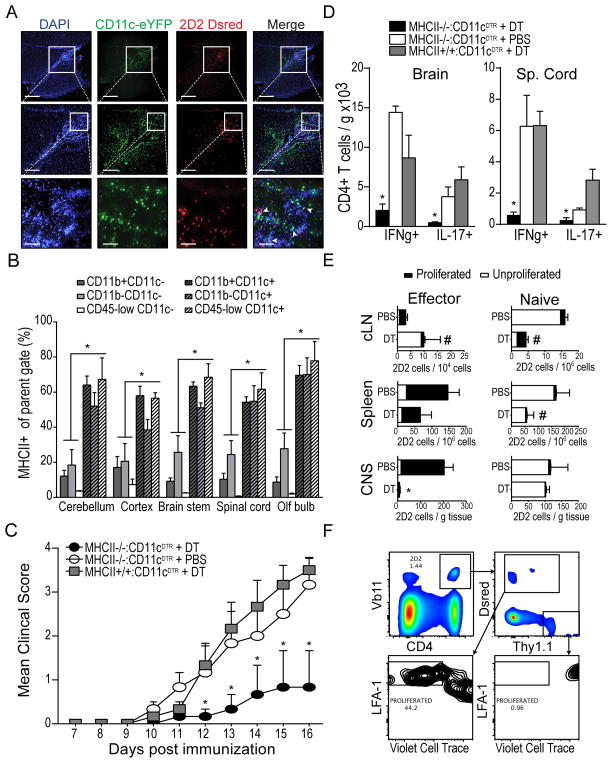
Figure 6. MHC class II expression on CNS-infiltrating DCs contributes to proliferation, recruitment, and cytokine production by co-infiltrating, myelin specific effector T cells.
A) Fluorescent micrographs of DAPI-stained sagittal brain sections showing developing peri-ventricular inflammatory lesions in CD11c-eYFP mice after adoptive transfer of purified CD4+ MOG-specific 2D2.Dsred T cells and EAE induction (DPI 12). CD11c-eYFP+ cells shown in green. 2D2.Dsred T cells shown in red. B) Frequency of MHC class II-expressing cells among various CD11c+ and CD11c− cell subsets isolated from CNS of CD11c-eYFP mice with EAE (DPI 12). C) Mean EAE clinical score is shown for groups (n =3) of WT mice reconstituted with mixtures of BM cells from the indicated donors. Mice were treated with diphtheria toxin (625ng/kg, i.p.) or PBS on DPI 8, 10, 12, and 14. D) Total number (per gram tissue) of spinal cord-infiltrating CD4+ T cells that produced IFNγ or IL-17 following 5 hour ex vivo restimulation with MOG35-55 peptide (20μg/mL). E) Pure FACS-sorted populations of MOG-specific naïve 2D2.Thy1.1 (CD4+ Vβ11+ CD62L+ CD44− Thy1.1+ Dsred−) or antigen-experienced 2D2.Dsred (CD4+ Vβ11+ CD62L− CD44+ Thy1.1− Dsred+) T cells were mixed together, labeled with violet cell trace, and adoptively transferred into congenic MHC II−/−:CD11c-DTR mice with EAE (DPI 9). Recipient mice were treated with either diphtheria toxin (625ng / kg, i.p.) or PBS on DPI 8, 10, 12, and 14. Bar graphs show frequency of proliferated (LFA1-high violet cell trace-low) and unproliferated (LFA1-low violet cell trace-high) transferred 2D2 T cells in cervical lymph node, spleen, and CNS tissues (expressed per gram tissue). Gating of transferred cells is shown in (F). *p < 0.05 Student’s t test. Error bars indicate s.e.m.