Figure 3. Blocking of NF-κB signaling increases the sensitivity of androgen-independent PCa cells to the anti-androgen.
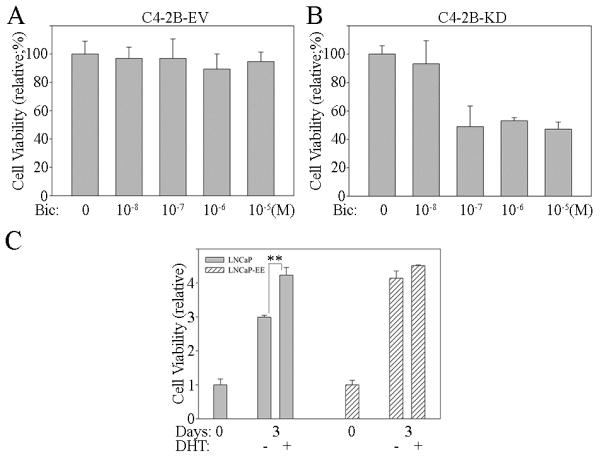
C4-2B cells were stably infected with IKK2-KD retroviral vector (C4-2B-KD), in which NF-κB activity was inhibited with a kinase dead (KD) IKK2 mutant. The cells infected with empty vector (EV) were used as controls leaving NF-κB signaling activated (C4-2B-EV). Both A) C4-2B-EV and B) C4-2B-KD cells were treated with Bicalutamide (Bic). Cell proliferation assay was performed at 48 hours after treatment. Results are presented as means ± SD of 3 experiments performed in triplicate. C) NF-κB signaling activated (LNCaP-EE) and inactivated (LNCaP-EV) LNCaP cells were treated with or without androgen (DHT; 10−8M). Cell proliferation assay was performed at 72 hours after treatment. Results are presented as means ± SD of 3 experiments performed in triplicate. **, P < 0.001 by Student’s t test.
