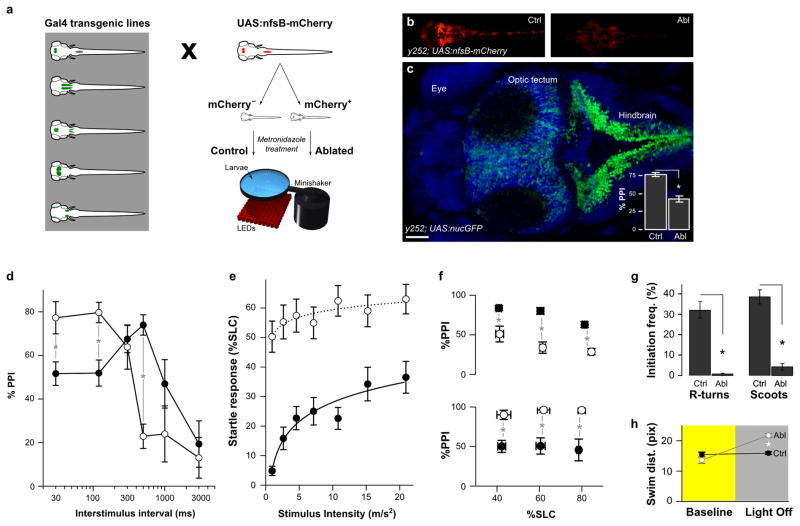
Figure 1. Neurons that modulate startle sensitivity and prepulse inhibition are identified by enhancer trap line y252.
(a) Schematic of the screen used to identify neurons required for PPI. Gal4 enhancer trap lines were crossed to a UAS:nfsB-mCherry transgenic line and sorted into mCherry expressing and non-expressing groups. Both groups were treated from 3–5 dpf with metronidazole for ablation of nitroreductase-mCherry expressing neurons. Behavioral testing was performed after 24 h recovery from the treatment. For screening, a 500 ms ISI was used.
(b) y252; UAS:nfsB-mCherry larvae maintained in embryo medium (ctrl) or in medium supplemented by 10 mM metronidazole for 48 h (ablated).
(c) Dorsal confocal projection of y252; UAS:nls-GFP larva showing the distribution of neurons expressing the Gal4 transgene (green), counterstained with DAPI (blue). Inset shows the mean and standard error of %PPI values for y252 control (N=47) and ablated (N=48) larvae. * P < 0.001. Scale bar 50 μm.
(d) Changes in PPI at different ISIs after neuronal ablation in y252; UAS:nfsB-mCherry larvae (open circles) compared to sibling controls (filled). N= 15–32 larvae per group. ANOVA significant interaction between ablation status and interstimulus interval F5,257 = 10.23, p < 0.001. # p < 0.05. * p < 0.01.
(e) Startle responsiveness (percentage of fish initiating a short latency c-start response, %SLC) in y252 ablated larvae (open circles, N = 41) compared to sibling controls (filled, N = 27). Main effect of ablation F1,66 = 26.58, p < 0.001. Comparisons between ablated and controls at all stimulus intensities are significant, p < 0.001.
(f) PPI at 500 ms ISI (top) and 30 ms ISI (bottom) in subsets of y252 ablated larvae (open circles) and sibling controls (filled) with similar startle responsiveness. Larvae were binned according to startle responsiveness (%SLC) in three groups: 30–50, 51–70 and 71–90. N=16–47 larvae per group. t-test * p < 0.01.
(g) Reduced locomotor activity after y252 ablation. Larvae initiate two types of swimming movements, routine turns (R-turns) and slow swims (scoots) both of which are significantly reduced. N = 5 groups controls, 3 groups ablated larvae. * p < 0.001.
(h) Distance travelled (pixels) per swim bout in y252 ablated larvae (Abl, grey) and controls (Ctrl, black) during baseline activity (yellow background) and movement in response to sustained darkness (grey background). N=36 larvae each group. * p < 0.001.