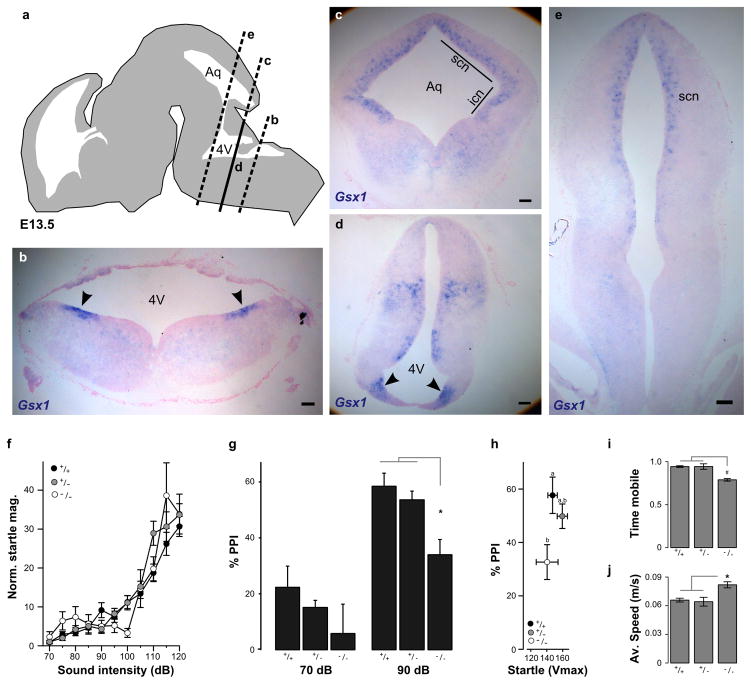
Figure 5. Gsx1 is required for PPI in mammals.
(a) Schematic of E13.5 mouse embryonic brain showing coronal planes of section through the brainstem for RNA in situ hybridization with Gsx1 probe in (b–e).
(b) Dorso-lateral expression domains of Gsx1 at the ventricular zone of the neuroepithelium in caudal hindbrain (arrowheads).
(c) Coronal section at the level of the aqueduct (Aq) showing expression of Gsx1 in ventricular zone of the superior colliculus (scn) and inferior colliculus (icn).
(d) Same plane of section as in (c) through the 4th ventricle (4V) showing Gsx1 expression at the ventricular zone of the pons (arrowheads).
(e) Rostral brainstem section showing Gsx1 expression in the ventricular neuroepithelium of the superior colliculus (scn). Scale bars (b–e) 100 μm.
(f) Startle magnitude in Gsx1 knockout mice and littermates, normalized by body weight (Vmax/g). Knockouts (open circles, N=10) show similar startle sensitivity to wildtype (black, N=15) and heterozygotes (grey, N=14).
(g) PPI in Gsx1 knockout mice (N=13) compared to wildtype (N=17) and heterozygous siblings (N=33) at a 100 ms ISI at the indicated prepulse intensities. Repeated measures ANOVA F1,61 = 4.99, p = 0.029. Genotypes are indicated. * p < 0.01.
(h) PPI in subgroups of mice from (g) with similar startle magnitudes (not adjusted for body weight), using mice with a mean response magnitude of between 100 and 200 (Vmax). ANOVA for genotype F1,28 = 6.49, p = 0.017. Posthoc homogeneous subsets are indicated.
(i–j) Locomotor activity in novel open field. Fraction of time (5 minute trials) spent mobile (i) and average speed during mobile periods (j) for wildtype (N=23), heterozygous (N=31) and homozygous Gsx1 knockout mice (N=16). # p < 0.05. * p < 0.01.