Figure 2.
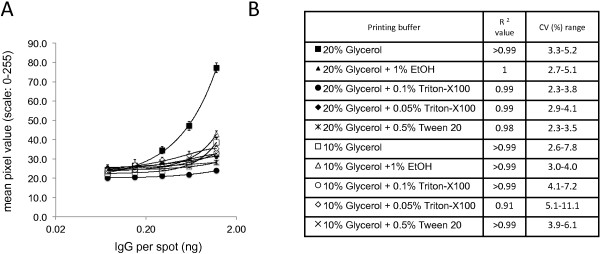
Effects of different printing buffers on the detection of human IgG printed on nitrocellulose. Various amounts of human IgG (1.2, 0.6, 0.3, 0.15 and 0.075 ng /spot) were printed on Whatman Protran BA-85 (0.45 μm) membrane using various printing buffers. Printed IgG was visualised in spot-ELISA and signals quantified by determining the pixel intensities of digitized spots. Panel A: Each line on graph represents the analyses results of printed IgG in different printing buffer consisting of PBS + 10% glycerol supplemented with either 0.1% or 0.05% Triton X-100, 0.5% Tween-20, 1% ethanol or nothing, or printing buffer consisting of PBS + 20% glycerol, supplemented with either 0.1% or 0.05% Triton X-100, 0.5% Tween-20, 1% ethanol or nothing (see Panel A for details). Each data point consists of measurements of five spots on five different strips (N = 25 per data point). X-axis: human IgG amount per spot. Y-axis: Staining intensity defined as the mean pixel intensity measured on a 0–255 grey scale. Panel B: R2 and CV (Coefficient of variation) value presented for each tested printing buffer.
