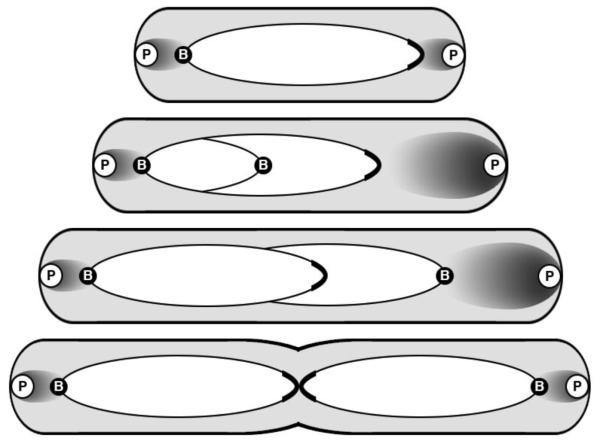
Figure 1.
Model of parABS-mediated segregation of V. cholerae chr1. The chromosome is represented by an ellipse, whose major axis has the ParB1 bound centromere (B) at one end and the replication terminus region (capped) at the other. In newborn cells, the centromere is found anchored to the old pole by the HubP (P) trans-membrane polar protein via ParB1, ParA1 and HubP interactions. ParA1 is shown as a cloud whose density is maximal near the pole. After replication initiation and duplication of the nearby centromeric region, one of the daughter centromeres migrates towards the new pole where ParA1 is present at higher concentration, shown by a larger cloud. The cloud meets the ParB1/parS1 centromeric complex when replication elongation has progressed further. The complex is then rapidly pulled to the pole by retraction of the ParA1 cloud. In predivisional (mother) cells, the terminus region is found together at midcell. Adapted from [Fogel and Waldor, 2006; Srivastava et al., 2006; Yamaichi et al., 2012].