Figure 3.
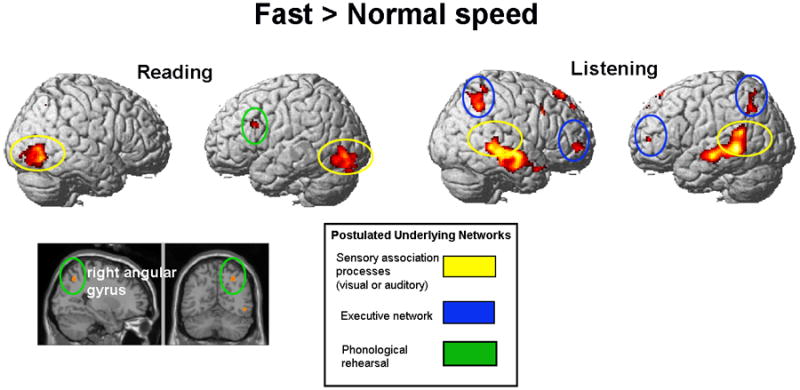
Faster comprehension: increased activation in visual and auditory association cortices. Fast presentation > normal presentation contrast for reading and listening comprehension (collapsed across familiarity). Speed reading (Experiment 1): left inferior frontal and right angular gyri, and bilateral occipital lobe. Speed listening (Experiment 2): bilateral dorsolateral prefrontal, parietal, and temporal cortices. SPM2; clusters significant at p < .001, uncorrected, extent threshold = 20 voxels, t = 4.14 for reading comprehension (n = 11); t = 4.50 for listening comprehension (n = 9). Postulated networks: (1) sensory association processes, visual or auditory (e.g. Michael et al., 2001); (2) executive network: (Crottaz-Herbette et al., 2004; Mason & Just, 2006; Smith et al., 1998; Smith & Jonides, 1998); (3) phonological rehearsal (e.g. Buchweitz et al., 2009).
