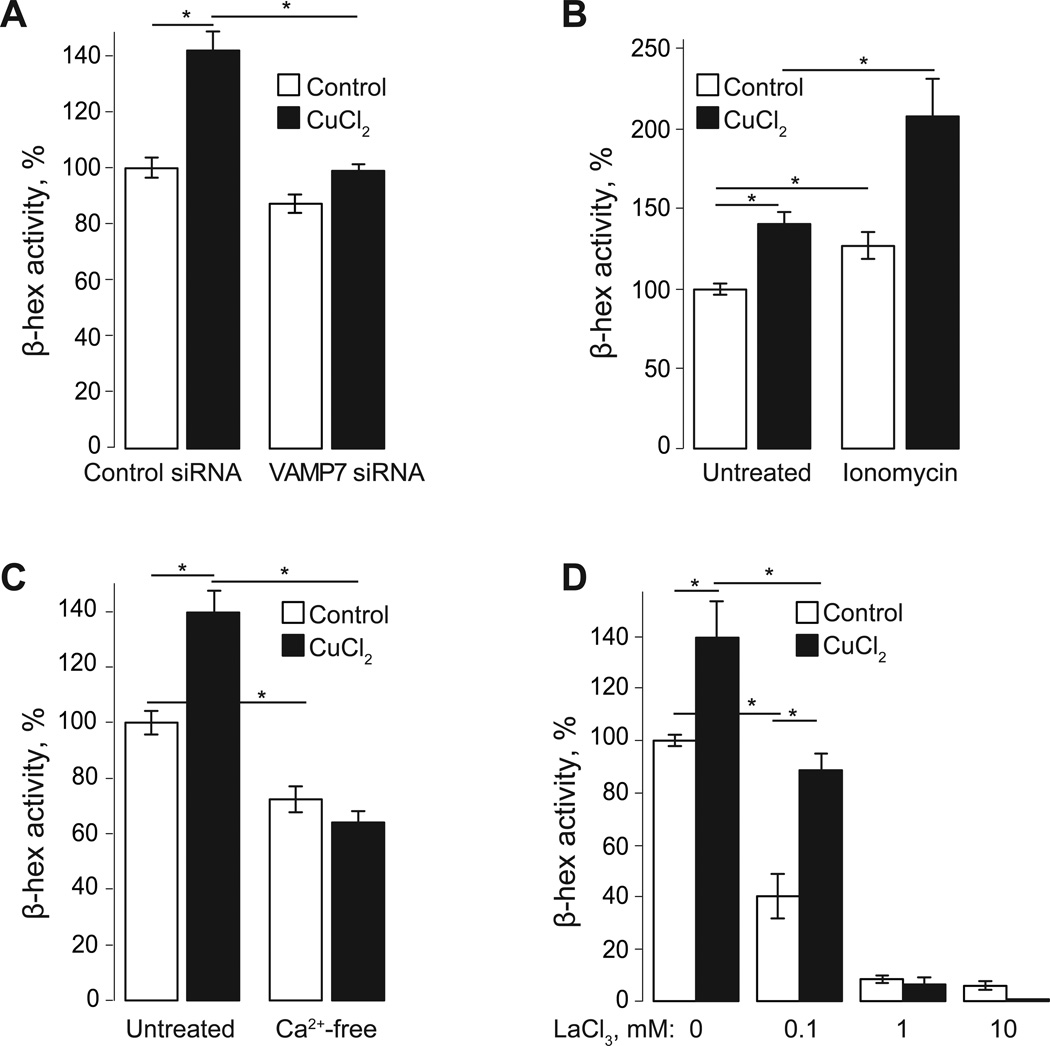
Fig. 2. Cu increases VAMP7 and Ca-dependent lysosomal exocytosis.
A. HeLa cells were transfected with VAMP7 or control siRNA 48 hours before the experiment was performed. Cells were treated for 1 hour with 100 µM CuCl2 in regular buffer or left untreated. β-hex activity was measured in extracellular medium at 1 hour. VAMP7 siRNA reduces both basal and Cu-induced lysosomal exocytosis. B. Addition of the Ca ionophore, ionomycin, for 15 min increased both basal and Cu-induced lysosomal exocytosis, observed as a decrease in β-hex activity in extracellular buffer at 1hour. C, D. Extracellular Ca is required for lysosomal exocytosis. Incubation of cells in Ca-free buffer reduced β-hex activity in extracellular medium and prevented Cu-induced exocytosis after 1hour (C). Addition of LaCl3 reduced lysosomal exocytosis in a dose-dependent manner. Cells were exposed to 0.1, 1, and 10 mM LaCl3 for 1 hour in the presence or absence of Cu (D). Values represented as mean ± SEM percent of β-hex activity in control cells (untreated); three independent experiments; statistical significance was calculated using a two-tailed, unpaired t-test with p<0.05 (*).