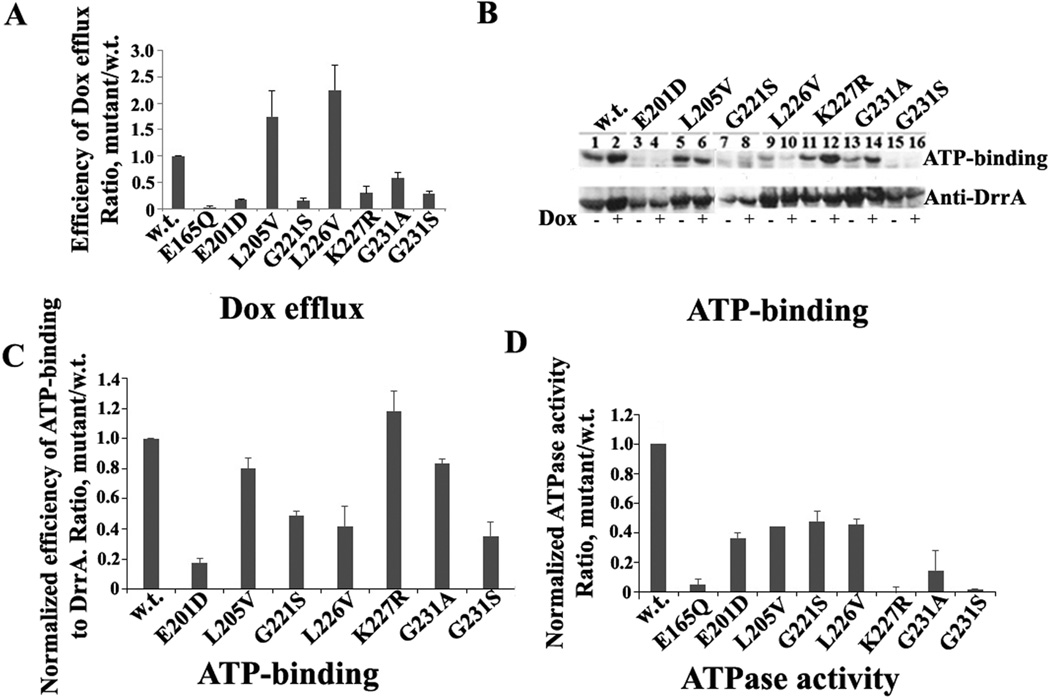
Fig. 2.
Functional analysis of GATE mutants. A, effect of point mutations in GATE on Dox efflux by DrrAB. The background efflux obtained with empty vector was subtracted from WT and mutants. Efflux efficiency was calculated as the mutant slope/WT slope within one set, designating WT efficiency as 1. B, effect of GATE mutations on ATP-binding to DrrA. Top, a representative autoradiogram showing ATP binding to cell membranes containing WT DrrAB and GATE mutants. Bottom, Western blot analysis of samples from above. C, histogram showing ATP binding efficiency to GATE mutants. D, histogram showing the effect of GATE mutations on ATP hydrolysis. Data in Fig. 2A, C, and D represent an average of three independent experiments with error bars showing standard deviation.