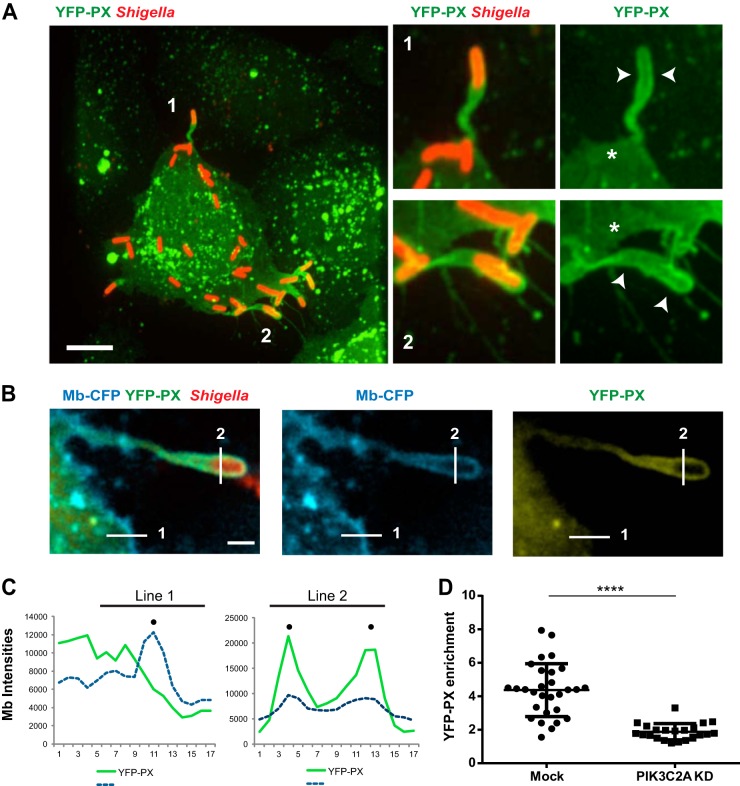
FIG 5.
PIK3C2A supports PtdIns(3)P production in membrane protrusions in HT-29 cells. (A) Representative image (left panel) of HT-29 cells transfected with the YFP-tagged PtdIns(3)P-binding PX domain construct (YFP-PX, green) and infected with RFP-expressing S. flexneri (red). Bar, 5 μm. The panels on the right show high-magnification images of the bacteria labeled 1 and 2 in the left image. Arrowheads indicate the recruitment of the YFP-PX probe to the membrane surrounding protrusions, and asterisks indicate the absence of the probe at the plasma membrane next to the protrusions. (B) Representative image of a protrusion formed in CFP membrane marker-expressing HT-29 cells (cyan) expressing the YFP-PX probe (yellow) and infected with RFP-expressing S. flexneri (red). Bar, 2 μm. (C) Graph showing line profile analysis of the signal corresponding to CFP membrane marker and the YFP-PX probe in the cytosol and at the plasma membrane (line 1) and in the protrusion membranes (line 2) as shown in panel B. (D) Graph showing statistical analysis of the relative enrichment of the YFP-PX probe in the protrusions formed in mock-treated (Mock) and PIK3C2A-depleted (PIK3C2A KD) HT-29 cells (****, P < 0.0001; unpaired t test).