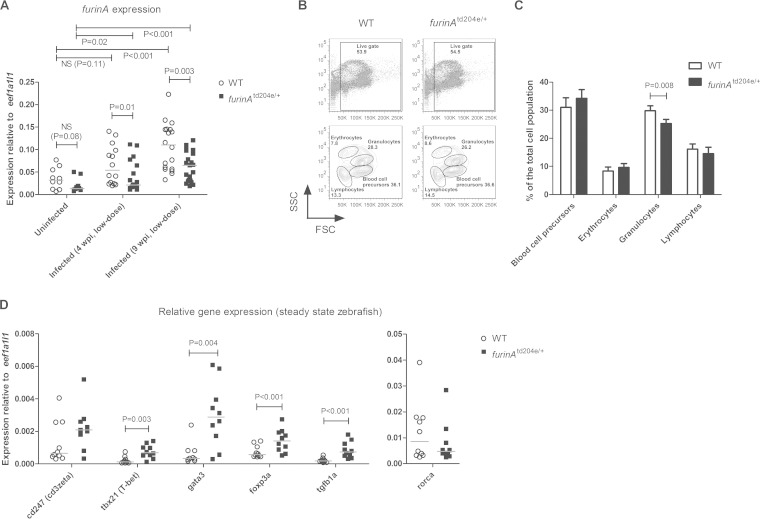
FIG 1.
furinA expression is reduced in furinAtd204e/+ zebrafish and associates with decreased granulocyte counts, as well as altered T helper cell subtype transcription factor expression. (A) Relative furinA expression was measured in uninfected (n = 10) and M. marinum-infected (at 4 and 9 wpi, low-dose, n = 13 to 21) furinAtd204e/+ mutant adult zebrafish and WT controls with qRT-PCR. Samples were run as technical duplicates. (B and C) The relative percentages of blood cell precursors, erythrocytes, granulocytes, and lymphocytes were determined in the kidneys of steady-state (uninfected) furinAtd204e/+ mutants and WT zebrafish (n = 5 in both groups) with flow cytometry, based on granularity (SSC) and cell size (FSC). Representative flow cytometry plots are shown in panel B. Gated populations are outlined, and the cell counts inside the gates are given as the percentages of the total viable cell population. The average relative percentages of different hematopoietic cell populations in mutants and controls are plotted in panel C (error bars indicate the standard deviations). (D) Relative expressions of different Th cell-associated genes (cd247, tbx21, gata3, foxp3a, and rorca), as well as tgfb1a, were quantified in furinAtd204e/+ mutants and WT controls (n = 10 in both groups) with qRT-PCR. Gene expressions in panels A and D were normalized to eef1a1l1 expression and represented as a scatter dot plot and median. In panel A, a one-tailed Mann-Whitney test was used in the statistical comparison of differences between furinAtd204e/+ zebrafish and WT controls, and a two-tailed Mann-Whitney test was used in panels C and D, as well as in the comparisons between uninfected and infected experimental groups in panel A.