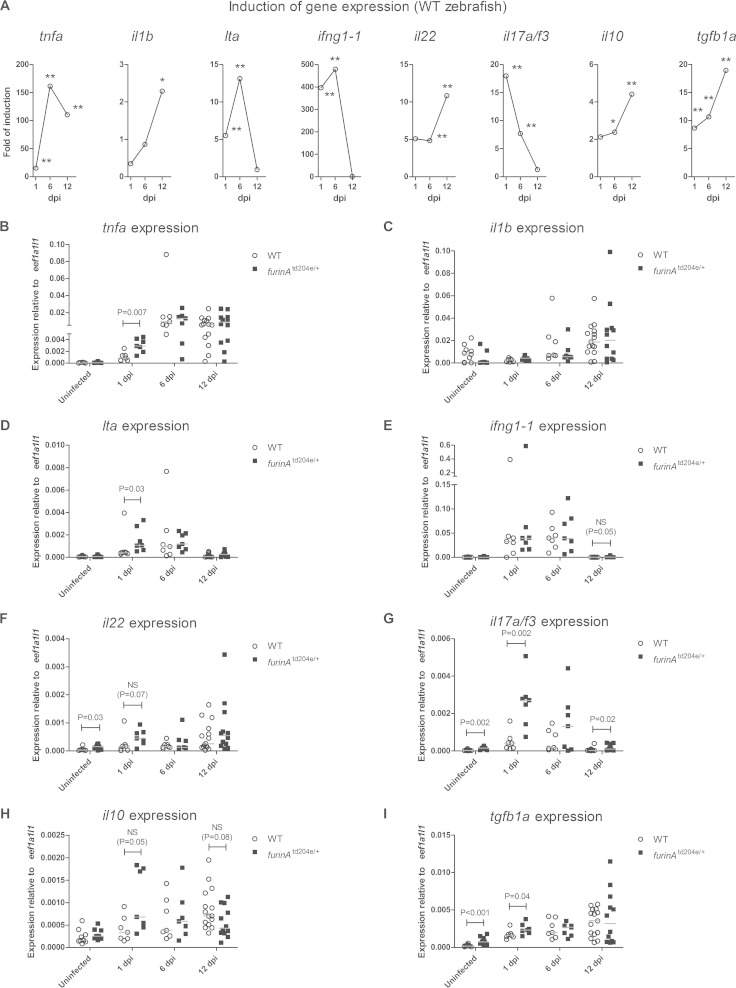
FIG 4.
FurinA attenuates the early expression of proinflammatory cytokine genes in an experimental high-dose mycobacterial infection. The relative expression of proinflammatory cytokine genes (tnfa, il1b, lta, ifng1-1, il22, and il17a/f3) and anti-inflammatory cytokine genes (il10 and tgfb1a) was determined in adult furinAtd204e/+ (n = 7 to 12) and WT (n = 7 to 15) zebrafish with qRT-PCR after a high dose of an M. marinum inoculate at 1, 6, and 12 dpi. (A) Fold gene expression induction median shown for all of the aforementioned genes in infected WT zebrafish. The fold induction was normalized to the gene expression median in uninfected zebrafish. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. (B to I) Relative gene expression in furinAtd204e/+ and WT zebrafish represented as a scatter dot plot and median. Note the different scales of the y axes and the divided y axis in panels B and E. Gene expressions were normalized to eef1a1l1 expression. At 1 and 6 dpi, samples were run as technical duplicates and uninfected, as well as 12-dpi, samples once. A two-tailed Mann-Whitney test was used in the statistical comparison of differences.