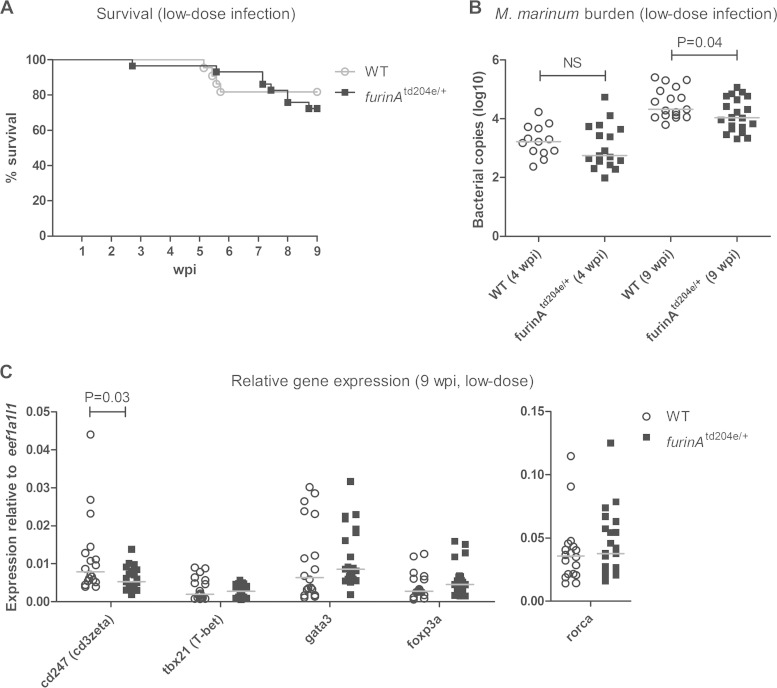
FIG 6.
Downregulation of furinA expression decreases the M. marinum burden and the T cell marker cd247 mRNA level in an experimental low-dose mycobacterial infection. A latent mycobacterial infection was induced with a low-dose M. marinum inoculate. (A) Survival of adult furinAtd204e/+ (n = 29) and WT (n = 22) zebrafish was monitored for 9 weeks. A log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test was used for the statistical comparison of differences. The data were collected from a single experiment. (B) The M. marinum burden of furinAtd204e/+ mutants (n = 17 to 20) and WT controls (n = 13 to 18) was quantified with DNA qRT-PCR at 4 and 9 wpi. Bacterial load is represented as the median of total bacterial copies (log10). M. marinum quantifications were run as technical duplicates. (C) The relative expression of Th cell markers (cd247, tbx21, gata3, foxp3a, and rorca) was quantified with qRT-PCR in furinAtd204e/+ mutants (n = 18 to 21) and WT controls (n = 18) at 9 wpi. Gene expressions were normalized to eef1a1l1 expression and represented as a scatter dot plot and median. Expression analyses were run as technical duplicates. In panels B and C, a two-tailed Mann-Whitney test was used in the statistical comparison of differences.