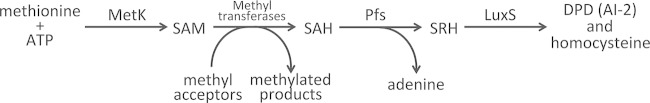
FIG 1.
Activated methyl pathway of B. burgdorferi. MetK synthesizes S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) from ATP and methionine. SAM then acts as a methyl donor for many metabolic steps, also producing the by-product S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH). SAH is toxic, so Pfs cleaves that molecule to produce adenine and S-ribosylhomocysteine (SRH). SRH is nontoxic, and some bacterial species, such as the spirochete Treponema pallidum, end the pathway at this step. B. burgdorferi instead uses LuxS to cleave SRH into homocysteine and 4,5-dihydroxy-2,3-pentanedione (DPD). Biochemical and genetic analyses demonstrated that B. burgdorferi lacks the ability to further metabolize homocysteine (7, 10). DPD, also known as autoinducer-2 (AI-2), is secreted by B. burgdorferi into the environment (7).