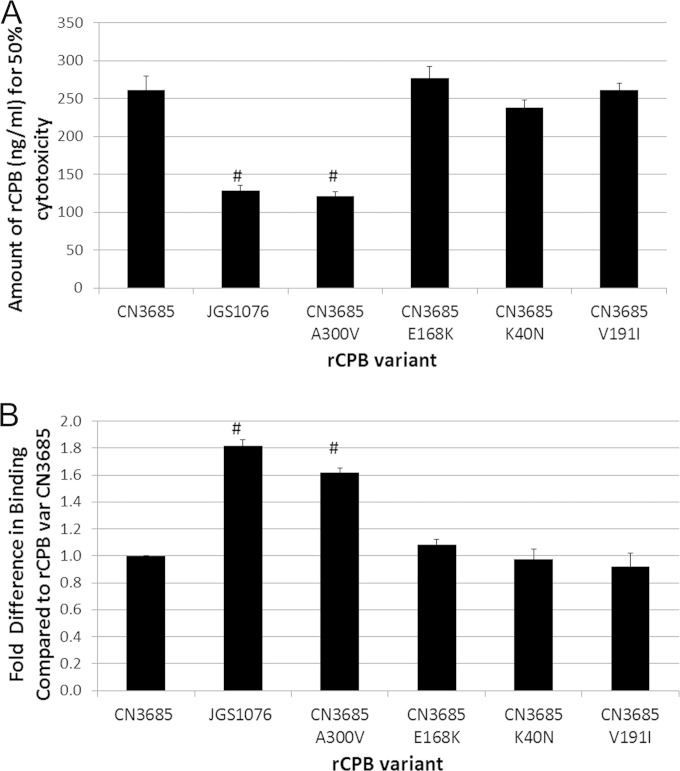
FIG 6.
Testing individual site-directed rCPB mutants for binding and cytotoxicity phenotypes. (A) Recombinant CPBs containing JGS1076 and CN3685 sequences were constructed in pGEX-2T as GST fusion proteins. Site-directed mutagenesis was performed on the CN3685 rCPB variant, switching each of the 4 amino acids that differ between CN3685 CPB and JGS1076 CPB to the amino acid present in the JGS1076 sequence. Cytotoxicity of purified rCPBs for HUVEC cells was determined after a 9-h treatment using an MTT cell viability assay. Mean amounts of rCPB necessary to cause 50% cytotoxicity in three replicate experiments are presented. (B) Purified rCPB from the site-directed mutants was added to HUVEC cell monolayers for 1 h, allowing for binding/complex formation. After rinsing to remove unbound rCPB, Western blotting and densitometry were used to determine the relative amounts of rCPB variants bound to host cells. Mean results from three independent experiments are presented as fold changes in binding compared to that of the CN3685 variant rCPB. #, there was a significant (P < 0.05) difference compared to the results for the CN3685 variant rCPB.