FIG 3.
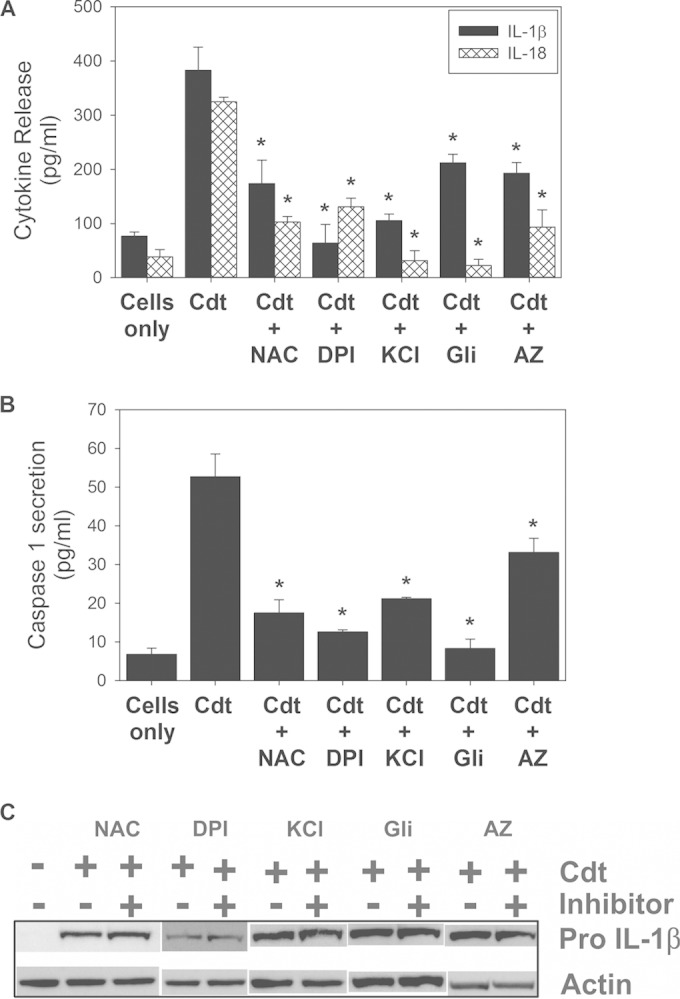
Cdt-induced inflammasome activation involves ROS, K+ efflux, and extracellular ATP. NAC (10 mM) and DPI (250 nM) were used to determine the requirement for ROS, elevated extracellular levels of K+ (70 mM) and glibenclamide (Gli) (50 μg/ml) were used to determine the requirement for K+ efflux, and AZ11645373 (AZ) (1 μM) was used to determine the requirement for an ATP-PTXR7 interaction. (A and B) Effects of these agents on Cdt (50 ng/ml)-induced production of IL-1β and IL-18 (A) and on caspase-1 release (B). Results are the means ± standard errors of the means for three experiments, each performed in triplicate; asterisks indicate statistical significance compared to the Cdt-only control (P ≤ 0.05). (C) Cells were also analyzed for the presence of pro-IL-1β by Western blotting. Actin is shown as a loading control.
