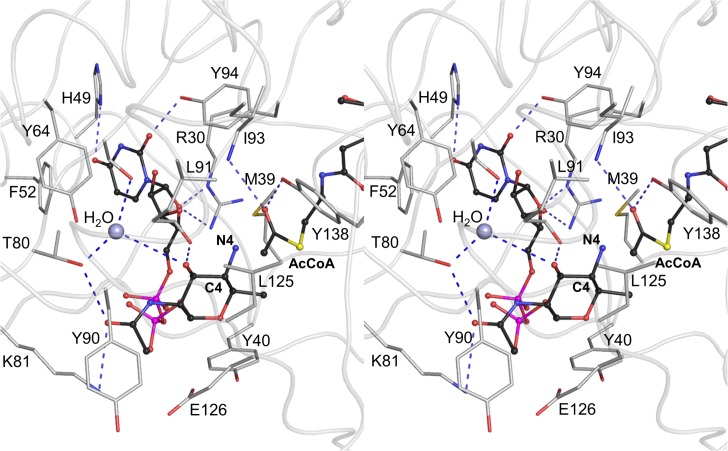
Fig 6. Interactions between the docked substrate UDP-4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-β-L-AltNAc, acetyl moiety of the cofactor and protein residues in the active site of PseH in the modeled Michaelis complex.
The protein backbone is shown as ribbon structure in light grey for clarity of illustration. The substrate and AcCoA molecules are shown in ball-and-stick CPK representation and coloured according to atom type, with carbon atoms in black, nitrogen in blue, oxygen in red, phosphorus in magenta and sulphur in yellow. Only the protein side-chains that interact with the substrate are shown for clarity. The C4-N4 bond of the substrate (labeled) is positioned optimally for the direct nucleophilic attack on the thioester acetate, with the angle formed between the C4 of the amino-altrose, N4 of amino-altrose and the thioester carbonyl carbon being approximately 120°. The water molecule that is hydrogen bonded to the side-chains of Ser78 and Thr80, and is located within a hydrogen-bond distance of the 3’-hydroxyl of the modeled 4’-amino-altrose, is represented as a grey-blue ball. Deprotonation of the substrate’s amine group may occur via the 3’-hydroxyl of the altrose and this intervening water molecule.