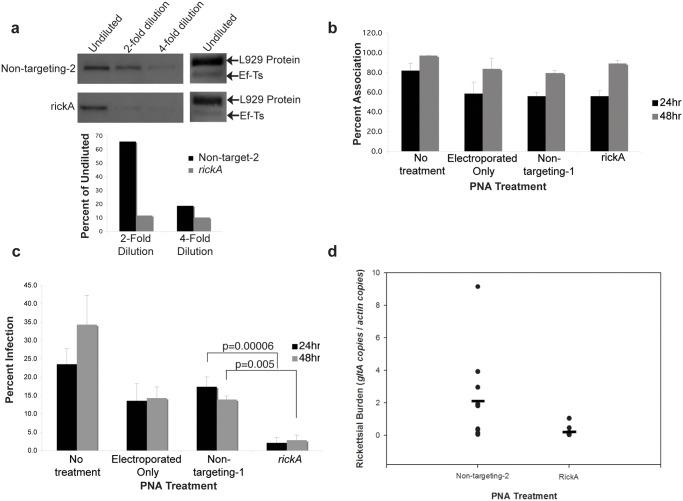
Fig 2. PNA decreases protein production and in vitro and in vivo infection by SFG R. montanensis.
A) Western blot of Opti-prep purified, serially diluted R. montanensis treated with rickA PNA and quantitative densitometry of the RickA expression as a percent of undiluted RickA. B) Adherence percentages and C) Infection percentages of L929 cells by R. montanensis treated with PNA designed to rickA at 24 and 48 hours. Infection by rickA PNA-treated R. montanensis is reduced 88% (p = 0.00006) at 24 hours and 80% (p = 0.005) at 48-hours post-infection. There is no statistically significant change in adherence with PNA treatment. In vitro experiments were repeated twice and performed in duplicate. Error bars represent standard deviation. D) Unfed D. variabilis adult ticks were injected with rickA PNA-treated (n = 11) or non-targeting control PNA-2-treated (n = 10) rickettsia. Rickettsial burden was measured using qPCR. Genomic copies for gltA were normalized to genomic copies for actin. Closed circles represent individual ticks and the closed horizontal bars represent the mean. Rickettsial burden in ticks infected with rickA PNA-treated R. montanensis is reduced 90% compared to the control (p = 0.004). In vivo experiments were repeated twice with 10 biological replicates per treatment.