Fig 1. Isolation of the element responsible for the low copy number limit in the DIE2 region.
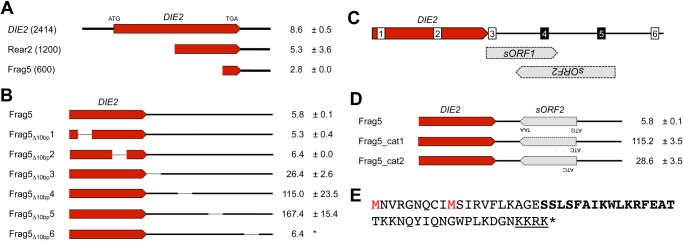
- Copy number limits of DNA fragments from the DIE2 region. The data were obtained from our previous study [1].
- Copy number limits of DNA fragments (Frag5 in A) with serial 10-bp deletions every 100 bp. The asterisk indicates that only single experiment was performed.
- Locations of the small ORFs (sORF1 and sORF2) in the 3′ region of DIE2. The numbers indicate the 10-bp deletions analyzed in B. The deletions shown in white did not affect the toxicity of the DNA fragment, whereas the deletion shown in black disrupted the toxicity.
- Copy number limits of DNA fragments with ATG to ATC substitutions in sORF2.
- Amino acid sequence of sORF2. The substituted methionines (ATG codons) in C are shown in red. A potential NLS sequence is underlined, and an amino acid sequence predicted to construct a helical structure is shown in bold letters.
