Fig. 5.
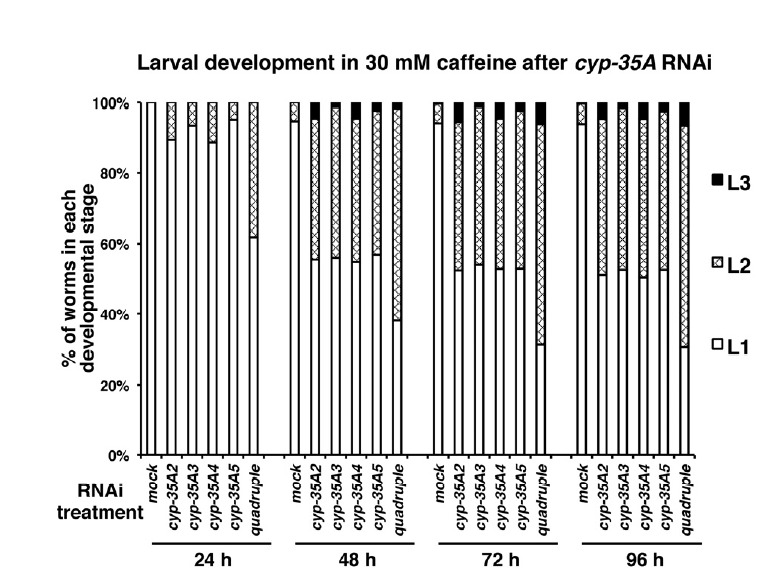
RNAi of cyp-35A family genes partially rescued larval developmental arrest caused by 30 mM caffeine treatment. N2 worms synchronized at the L1 larval stage were treated with soaking RNAi (single or quadruple RNAi) to deplete cyp-35A family gene activity. Worms were then transferred to 30 mM caffeine-containing NGM plates and cultured at 20°C. During the culture, larval development was scored in 24 h intervals for 96 h, and percent distribution of worms in each developmental stage was displayed as a percent distribution graph for each RNAi treatment and time point. About 450 individuals (triplicates of 150 individuals/plate) were scored for each RNAi treatment. Average values of percent distribution of worms at each developmental stage are summarized in Supplementary Table S3.
