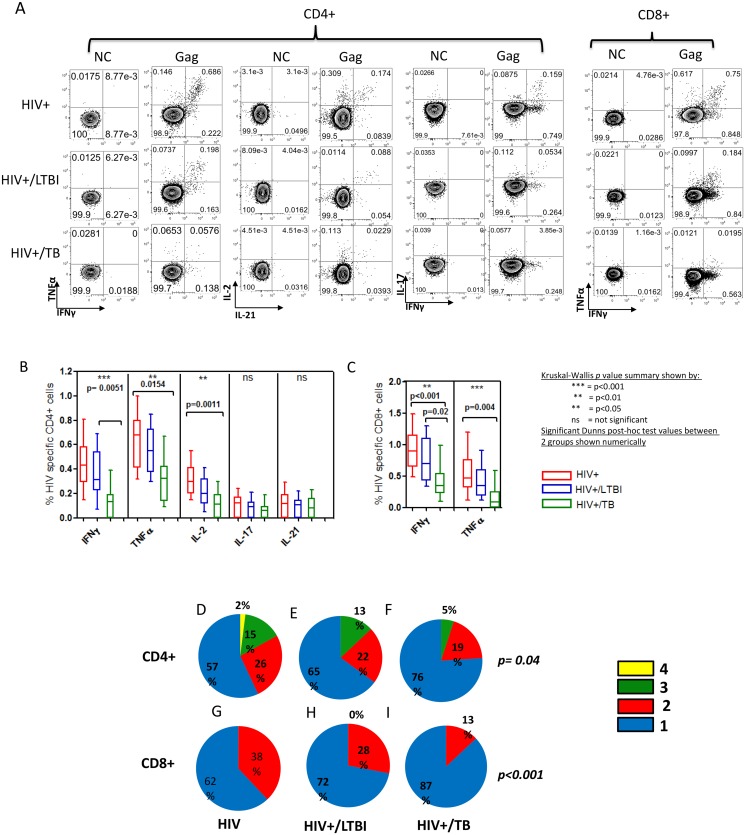
Fig 1. HIV specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell functionality is reduced in HIV infected individuals co-infected with latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection (LTBI) and active Tuberculosis (TB) disease.
(A) Representative flow cytometry plots showing cytokine responses for HIV (gag), control (no antigen) for HIV mono-infected subjects, and subjects co-infected with latent MTB infection (LTBI) and active tuberculosis (TB) (B) HIV-specific CD4+ release of IFNγ (p<0.001), TNFα (p<0.01) and IL-2 (p<0.01) were significantly different between all groups (Kruskal-Wallis). (C) HIV-specific CD8+ release of IFNγ (p<0.01) and TNFα (p<0.001) was significantly lower from HIV mono-infected subjects, to those co-infected with active TB. We additionally assessed the polyfunctionality profile of HIV specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in all patient groups. The polyfunctionality profiles between groups differed significantly for both CD4+ (p = 0.04) and CD8+ (p<0.001).(D) HIV-specific CD4+ T cells from HIV mono-infected subjects displayed a polyfunctional CD4+ T cell profile with a maximum of four functions being present (IFN+IL-2+IL-17+TNFα (2%)).(E) HIV-specific four function CD4+ T cells were not present in subjects co-infected with LTBI (F) Further decreases in HIV-specific CD4+ T cell polyfunctionality were observed in HIV positive subjects co-infected with TB, being replaced by a largely mono-functional profile with a decreased amount of triple cytokine cells (5% as compared to 13% in HIV/LTBI and 15% in HIV mono-infection). Additionally, single positive TNF-α cells dominated the profile (48%). (G) HIV-specific CD8+ T cells in HIV mono-infected subjects displayed a polyfunctional profile with a maximum of 2 functions being present (IFN+ TNFα (2%). (H) A maximum of 2 functions (IFN+TNFα+ (28%)) were present in HIV-specific CD8+ cells from subjects co-infected with LTBI. (I) 87% mono-functional cells were present in the HIV-specific CD8+T cell profile from subjects co-infected with TB, suggesting a complete loss of polyfunctionality.