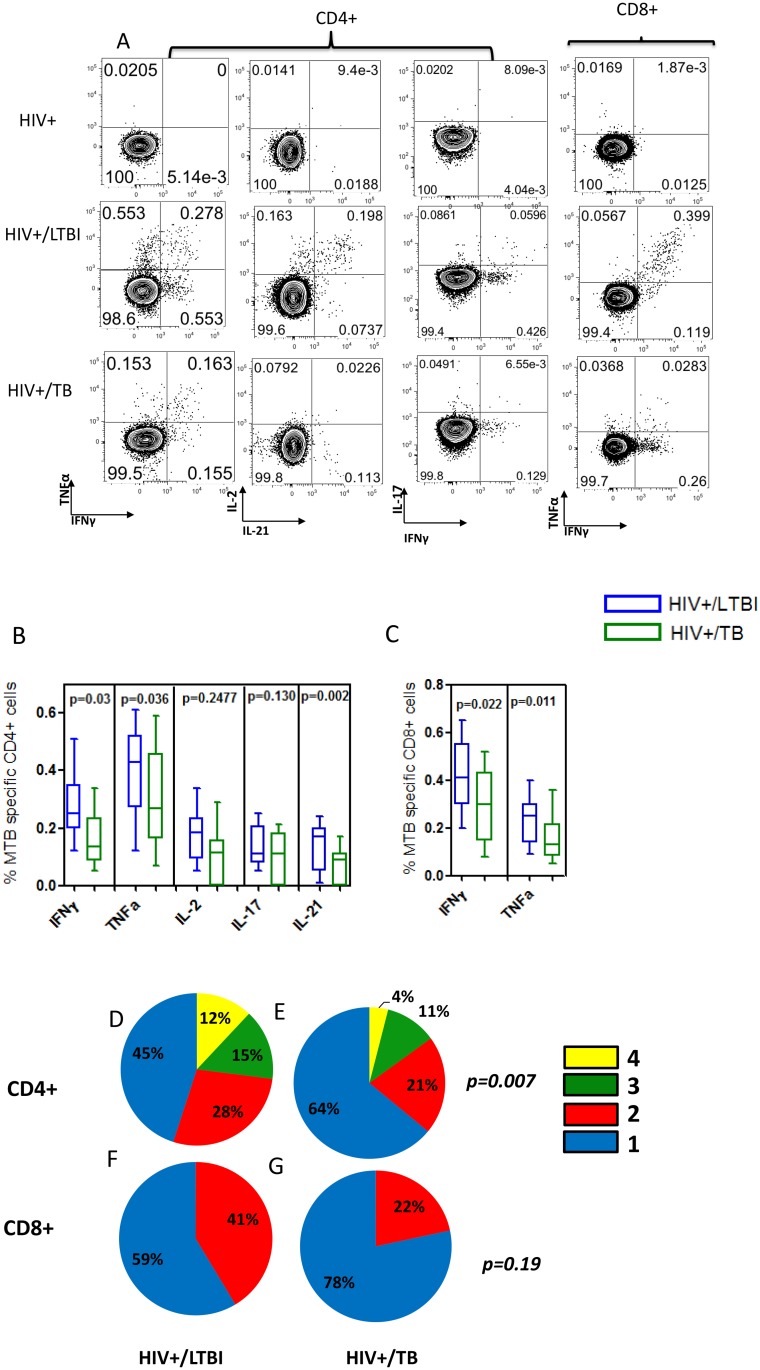
Fig 2. MTB-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell functionality is reduced in HIV infected individuals co-infected with latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection (LTBI) and active tuberculosis (TB) disease.
(A) Representative flow cytometry plots showing cytokine IFN-gamma and TNF-α response for Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) (CFP-10 and ESAT-6). Corresponding negative controls (no antigen) are the same as shown in Fig. 1B. (B) MTB-specific CD4+ release of IFNγ (p = 0.03), TNFα (p<0.03) and IL-21(p<0.002) were observed to be significantly lower from subjects co-infected with LTBI to those co-infected with TB. (C) MTB-specific CD8+ release of IFNγ (p = 0.022) and TNFα (p<0.011), were lower subjects co-infected with TB as compared co-infected with LTBI.
We next assessed the polyfunctionality profile of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB)—specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in HIV mono-infection and co-infection with LTBI or TB. (D). We observed significant difference between the polyfunctionality profiles of HIV+/LTBI and HIV+/TB groups for both CD4+ (p = 0.007) and CD8+ (p = 0.19). A highly polyfunctional MTB-specific CD4+ T cell cytokine profile was observed in HIV positive subjects co-infected with LTBI, which including the capacity to secrete four cytokines by 12% of MTB-specific T cells (IFN+IL-2+IL-17+TNFα (9%), or IFN+IL-21+IL-17+TNFα (3%)). (E) A decrease in the polyfunctional profile of MTB-specific CD4+ T cells was observed in HIV co-infection with TB, with an increased dominance in mono-functional TNFα producing cells (from 12% to 31%). (F) MTB-specific CD8+ T cells from HIV infected subjects co-infected with LTBI displayed a profile with a maximum of 2 functions being present (IFN+TNFα (41%)). (G) Mono-functional IFNγ and TNFα producing cells dominated the profile of MTB-specific CD8+ cells in HIV infected subjects co-infected with TB (at 78%). There was total loss of IL-2 function but IFNγ+TNF+ double positive cells were present (IFN+TNFα+ (22%)). An increased dominance in mono-functional TNFα producing cells was also observed (47%).