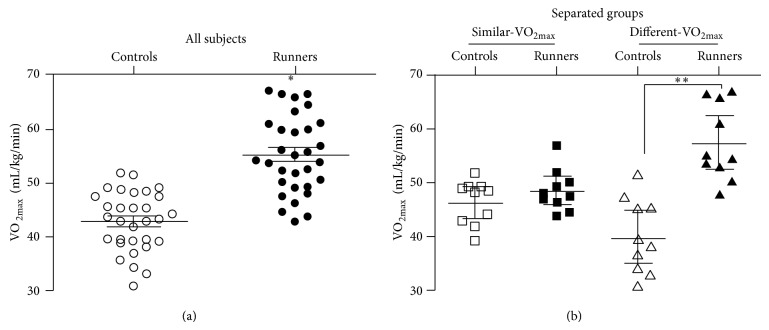
Figure 1.
VO2max (mL/kg/min) was determined in marathon runners and controls who were individually matched for age, BMI, and gender with one runner. Runners as a group had a significantly higher VO2max than their sedentary paired control (Panel (a)) (n = 31/group, P < 0.0001, t-test). When we stratified the pairs by difference in VO2max between each runner and their control the 10 pairs with the most similar-VO2max did not significantly differ in VO2max (Panel (b)) (n = 10, P = 0.22, t-test). In 10 pairs with the most different-VO2max the runners had a significantly higher VO2max (n = 10, P < 0.0001, t-test).