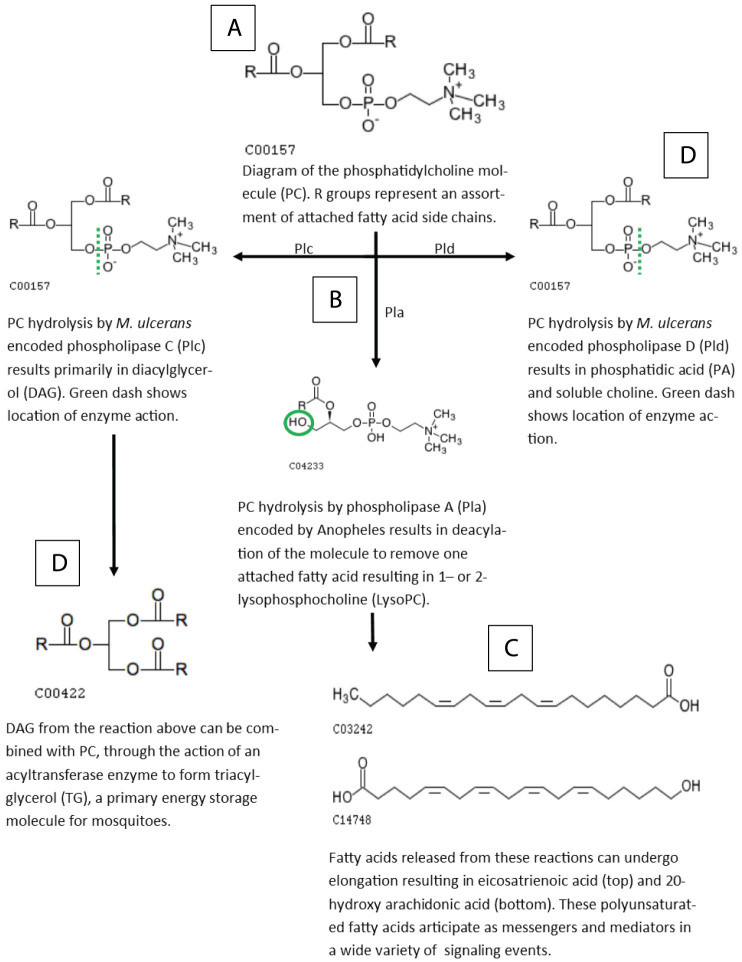
Figure 3. Phospholipids (PL) are a major constituent of biological membranes.
PL are characterized by a glycerol backbone attached to a phosphodiester group and a polar head group. Phosphatidylcholine (PC) is a functional class of PL molecule characterized by a choline head group. The fatty acid composition of PC can vary, but is generally composed of one saturated fatty acid and one unsaturated fatty acid, attached in the R position (A). Phospholipase hydrolysis of the PC molecule results in a plethora of subunits involved in many downstream signaling and metabolic processes (B). As PC molecules are cleaved by phospholipase A/B/C/D (Pla/b/c/d) (hashed lines), fatty acids are released (C), in addition to other cleavage products such as diacylglycerol (DAG), phosphatidic acid (PA), and choline (D). Fatty acids liberated from PC, DAG, TG, LysoPC can be elongated and/or modified to form ubiquitous signaling molecules. In this study, eicosatrienoic acid and 20-hydroxy eicosatetraenoic acid (hydroxy arachidonic acid) were found to be in lower abundance in groups exposed to M. ulcerans than controls. Molecular diagrams from Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (www.Kegg.jp/kegg/) [50, 51].