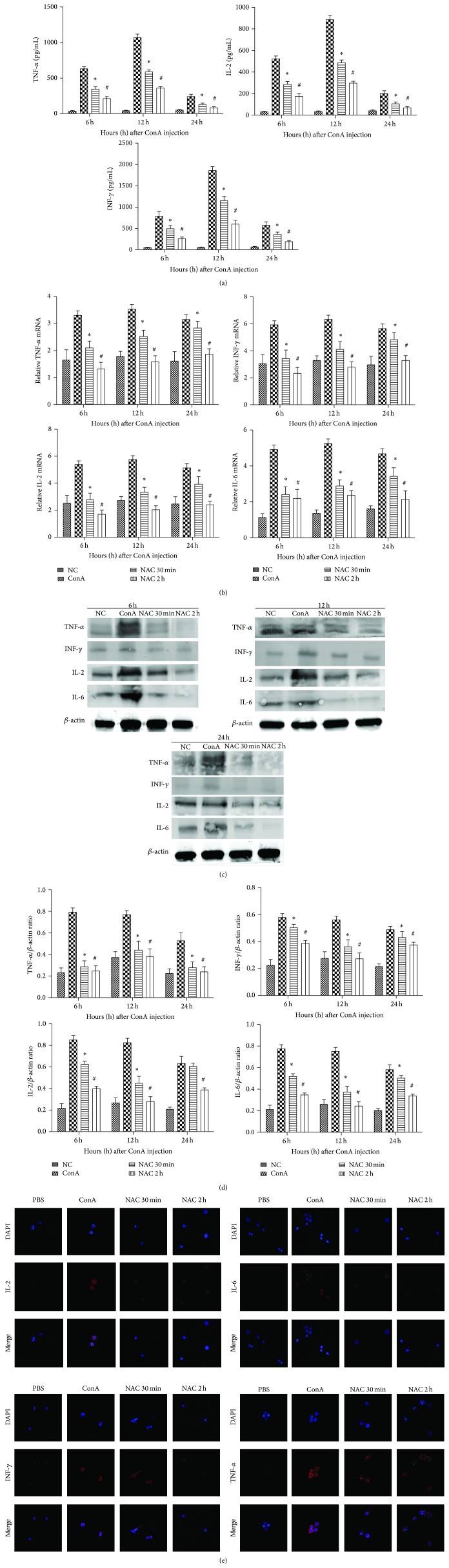
Figure 2.
NAC inhibits cytokines release in ConA-induced autoimmune hepatitis. (a) Serum levels of IL-2, IFN-γ, and TNF-α were measured by ELISA at 6 h, 12 h, and 24 h after ConA injection in mice. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 6; * P < 0.05 for ConA versus NAC 30 min (post-NAC-treated, 30 min after injection with ConA); # P < 0.05 for NAC 30 min (post-NAC-treated, 30 min after injection with ConA) versus NAC 2 h (NAC-pretreated, 2 h before injection with ConA)). (b) The expressions of IL-2, IL-6, IFN-γ, and TNF-α on mRNA levels were detected by real-time PCR. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 6; * P < 0.05 for ConA versus NAC 30 min; # P < 0.05 for NAC 30 min versus NAC 2 h). (c) The expressions of IL-2, IL-6, IL-1β, IFN-γ, and TNF-α on protein levels were detected with western blot. (d) The results of western blot were analyzed with Quantity One. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 6; * P < 0.05 for ConA versus NAC 30 min; # P < 0.05 for NAC 30 min versus NAC 2 h). (e) The differently expressions of IL-2, IL-6, IFN-γ, and TNF-α in macrophages' localization were evaluated by immunofluorescence (magnification is 630x).