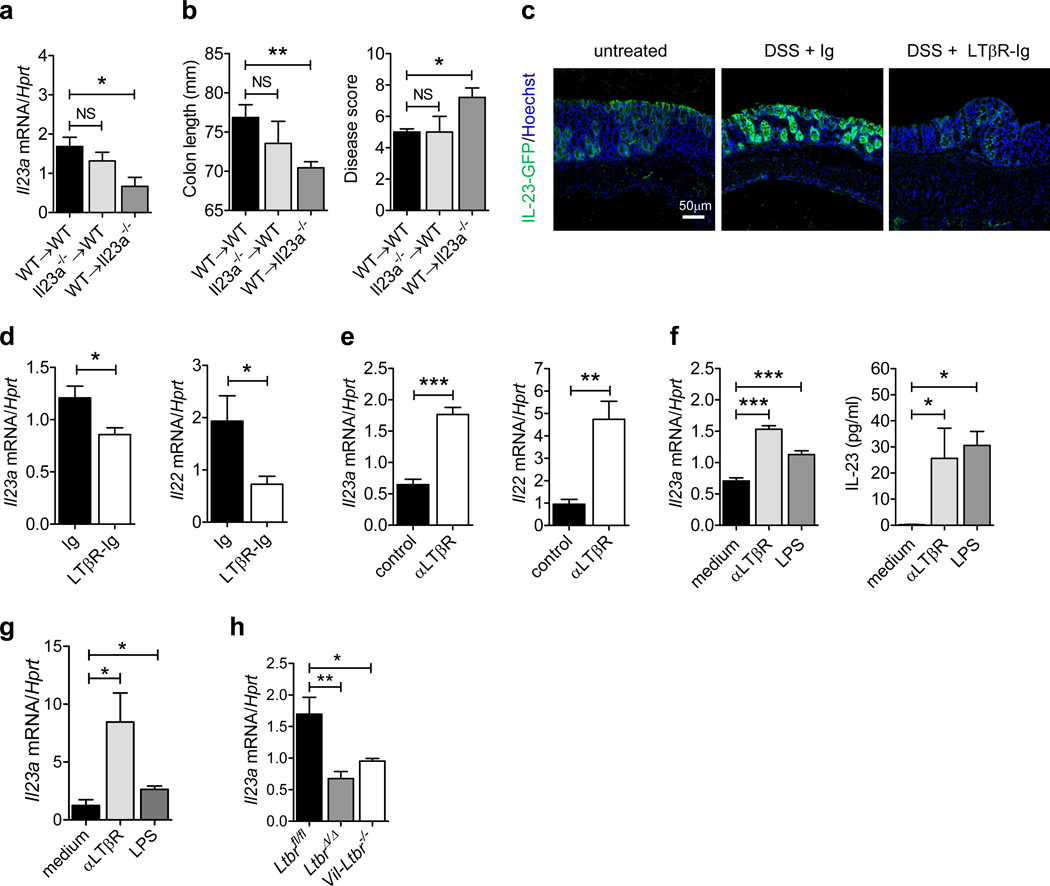
Figure 6.
Epithelial cells produce IL-23 in response to mucosal damage in a LTβR-dependent manner. (a and b) Bone marrow cells from C57BL/6 (WT) or Il23a−/− mice were transferred into lethally-irradiated WT or Il23a−/− mice. Six weeks later, WT→WT, Il23a−/−→WT and WT→Il23a−/− chimeric mice were treated for 5 days with 5% DSS. (a) Il23a mRNA expression in the colon of chimeric mice at day 5. (b) Colon length and clinical disease score at day 5. (c and d) Mice were treated for 5 days with 3.5% DSS or left untreated. LTβR-Ig fusion protein or control IgG was administered i.p. at days 0 and 3 (150 µg/mouse). (c) IL-23-driven GFP expression was evaluated at day 5 in the colon of IL-23-GFP+/− mice by GFP staining (green). Nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue). (d) Il23a and Il22 expression was evaluated in the colon of C57BL/6 mice at day 5. (e) C57BL/6 mice were treated for 5 days with 3.5% DSS. Agonistic αLTβR or control antibody was injected i.p. at days 0 and 3 (100 µg/mouse). Colonic Il23a and Il22 mRNA expression was evaluated at day 5. (f) CMT-93 epithelial cells were stimulated with agonistic αLTβR antibody (5 µg/ml) or LPS (1 µg/ml). Il23a mRNA expression and IL-23 protein production in culture supernatant was measured. (g) Il23a mRNA expression in sorted EpCAM + CD45− colon epithelial cells from WT mice, stimulated in vitro with agonistic αLTβR antibody (5 µg/ml) or LPS (1 µg/ml) for 12h. (h) Il23a mRNA expression in sorted EpCAM+ CD45− colon epithelial cells at day 5 after DSS treatment. For mRNA expression, data are normalized to Hprt. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 (Student’s t-test (a, b, d, e, f left panel, g, h) or two tailed Mann-Whitney test (f right panel)). Data are representative of two independent experiments with 3–7 mice per group. Error bars represent SEM.