Figure 3.
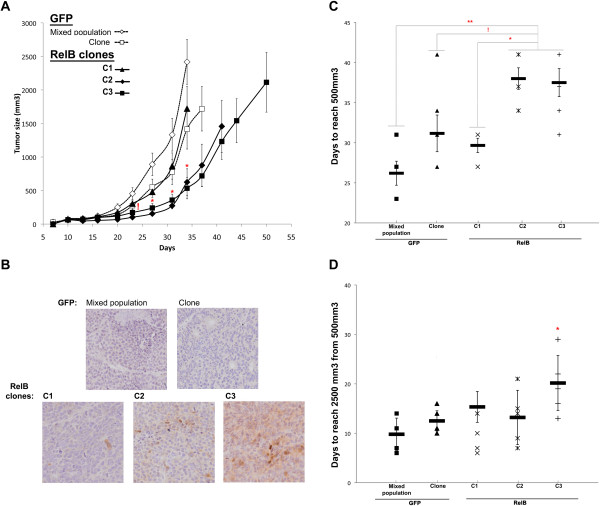
RelB expression effect on 22Rv1 induced-tumor formation in a SCID mouse model. Analysis of 22Rv1-induced tumor growth. 250,000 22Rv1 RelB or GFP cells suspended in matrigel solution (5 mg/mL) were injected subcutaneously in the flank of 6-weeks old SCID mice. For each 22Rv1 cell population, 6 mice were injected. A) Tumor size was graphically represented across time. For each group of mice, the last point of the curve corresponds to the time of the first mouse sacrifice. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. Significant variation between C2- and C3-RelB mouse groups individually compared to each GFP control (MP and clone) and C1-RelB mouse groups is illustrated by (*) on graph whereas (!) represents a significant variation between C2 and C3 RelB mice individually compared to MP GFP control group (Kruskal-Wallis test). B) Immunohistochemical staining of RelB illustrating its expression status on harvested 22Rv1-induced tumors. C) Time for 22Rv1-induced tumors to reach 500 mm3. On graph, (*) illustrated a p < 0.05; (**) p < 0.001. D) Time for 22Rv1-induced tumors to grow from 500 mm3 to 2500 mm3. (*) illustrates p < 0.05. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean (Anova one-way test followed by a Tukey post-test).
