Figure 4.
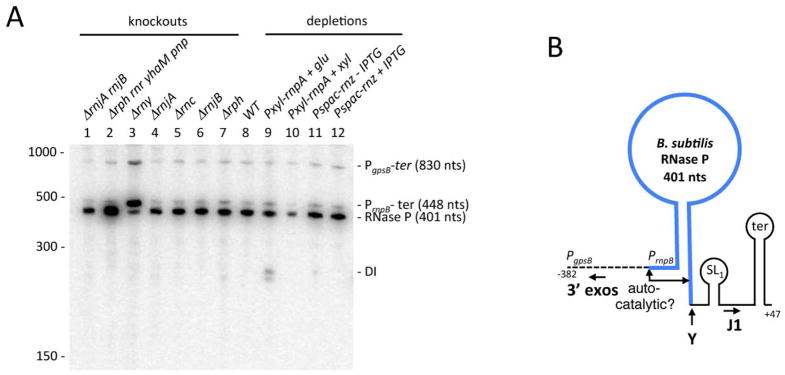
Processing and turnover of RNase P by different B. subtilis endo- and exoribonucleases. (A) Northern blot analysis of total RNA isolated from different B. subtilis RNase mutants probed for the 5′ end of the RNase P RNA (oligo CC1006). Gene symbols are as follows: rnjA (RNase J1), rnjB (RNase J2), rph (RNase PH), rnr (RNase R), yhaM (YhaM), pnp (polynucleotide phosphorylase), rny (RNase Y), rnc (RNase III), rnpA (RNase P protein subunit, rnpB (RNase P RNA subunit); rnz (RNase Z). The migration positions of RNA size markers are shown. The sizes of the intermediates are inferred from the sequence and confirmed with oligos specific for the 5′ ends of the PgpsB transcript and the transcription terminator (Fig. S3). (B) Processing pathway of RNase P. The mature sequence is shown in blue. The sites of autocatalytic cleavage observed in vitro in (Loria & Pan, 2000) are indicated. The locations of the transcription start sites from the PgpsB and PrnpB promoters are indicated. A Mulfold-predicted stem loop is labelled SL1 and the transcription terminator is labelled ter. Processing and degradation by RNases Y, J1 and the 3′ exoribonucleases (3′ exos) are indicated by larger bold-face type and arrows. The predicted sizes of the different fragments are indicated.
