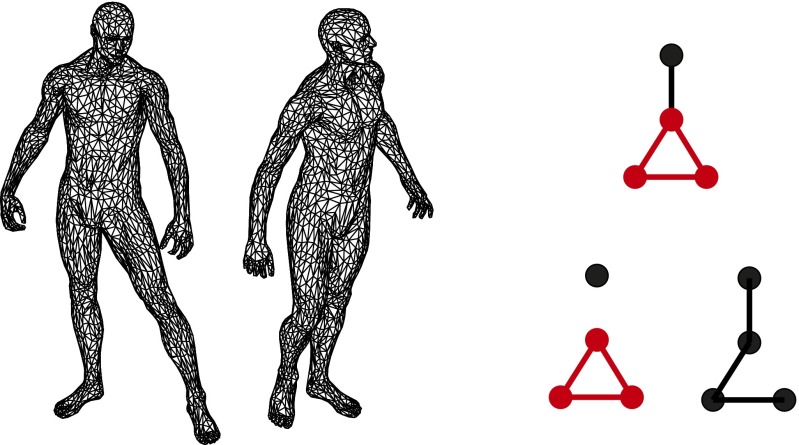
Fig. 1.
(Left) Two deformable shapes are represented as weighted graphs with edge weights proportional to the pairwise geodesic distances between the corresponding vertices. Optimal isomorphism in the sense of quantifies how isometric these two discrete metric spaces are and is related to the Gromov−Hausdorff distance (12). (Right) Limitation of the former distortion criterion. The bottom graphs are both 1-isomorphic to the top one, without distinguishing between exact partial isomorphism (Bottom Left; isomorphic subgraphs are marked in red) and inexact full isomorphism (Bottom Right).