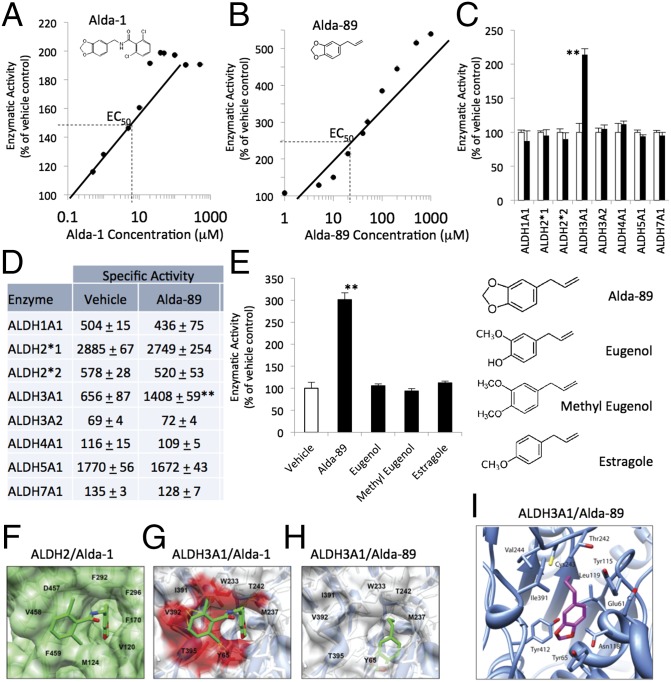
Fig. 1.
Selectivity of Alda-89 for ALDH3A1. (A) Structure and dose/response of Alda-1 activation of purified human recombinant ALDH2 and (B) Alda-89 activation of purified human recombinant ALDH3A1. Data are from three independent assays for each concentration, using NAD+ (2.5 mM) as a cofactor and 10 mM acetaldehyde as a substrate. (C) Alda-89 (20 μM) selectively activates ALDH3A1 and not seven other ALDH enzymes (5–20 μg of each enzyme, using 10 mM acetaldehyde as a substrate); data are presented as percentage of control (n = 3; **P < 0.01; bars represent the mean ± SD). (D) Same as C, but data are expressed as specific activity (μmole NADH/min/mg protein). (E) Structure activity relationship of Alda-89, eugenol, methyl eugenol, and estragole analogs (each at 50 μM) for ALDH3A1 activation. (F) Cocrystal structure of ALDH2 (green surface) with Alda-1 (green sticks) (PDB ID code 3INJ). (G) Superimposition of Alda-1 (green sticks) with clashing residues (red surface) from crystal structure of ALDH3A1 (blue ribbon/white surface; PDB ID code 3SZA). (H) A docking model of ALDH3A1 (blue ribbon/white surface) with Alda-89 (green sticks). (I) A modeled complex of ALDH3A1 with Alda-89. The position of Alda-89 was determined using DOCK 6.5. Electrostatic interactions and global constraints were calculated. Alda-89 (purple sticks, with the two oxygens labeled in red) is located within the enzymatic cavity. Cys243 (yellow stick) is the catalytic cysteine in the enzymatic cavity.