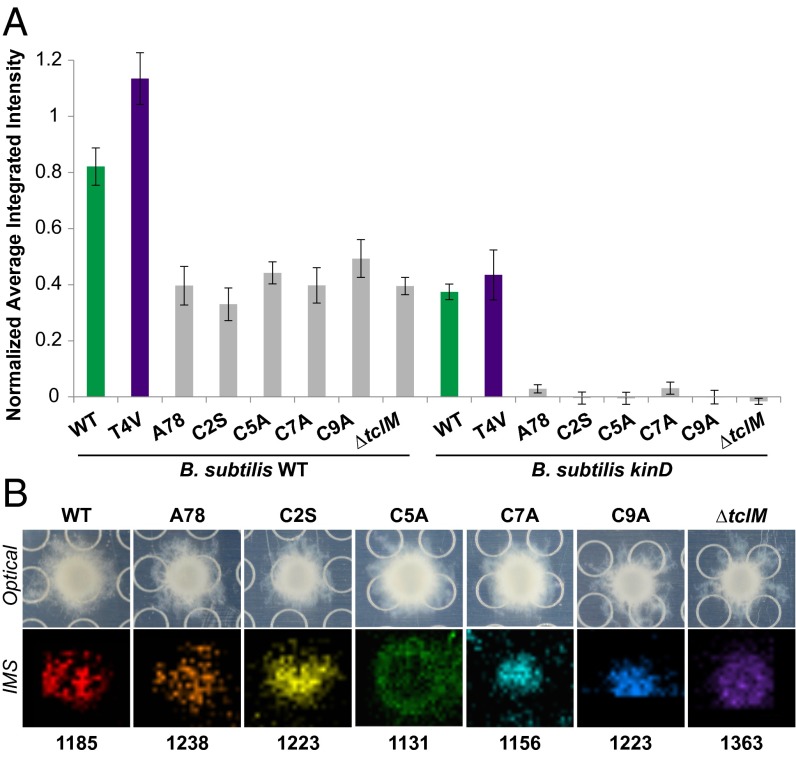
Fig. 5.
Structural modifications to thiocillin abolish its matrix-induction activity. (A) Quantification of fluorescence intensity of thiocillin mutant producers spotted onto a lawn of B. subtilis WT (Left) or kinD PtapA–yfp (Right) microcolonies (n = 3). None of the mutants (gray bars) were significantly different from one another on either the WT or kinD B. subtilis lawns, but each were significantly different from both WT and T4V B. cereus (by at least P < 0.05 on WT and at least P < 0.0001 on kinD). (B) Images of B. cereus colonies producing the mutant thiocillins indicated grown on agar on a MALDI plate with corresponding IMS data; colors represent ions of m/z indicated: WT [M+H+Na]+; A78 [M+H+Na]+; C2S [M+Na+K]+; C5A [M+H]+; C7A [M+H+Na]+; C9A [M+H+Na+K]+; ∆tclM [M+H]+.