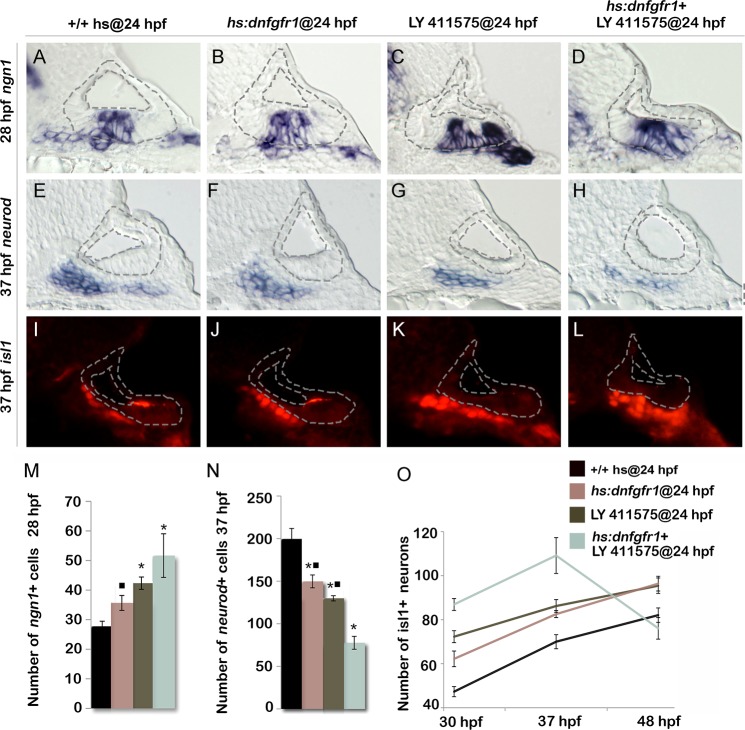
Fig 7. Reducing Fgf and Notch levels mimics the effects of tfap2a overexpression.
(A-L) Cross-sections (medial left, dorsal up) passing just posterior to the utricular macula and showing expression of ngn1 at 28 hpf (A-D), or sections passing through the utricular macula and showing neurod at 37 hpf (E-H) or Isl1 at 37 hpf (I-L) in wild-type control (A, E, I), hs:dnfgfr1 embryos (B, F, J), LY411575 inhibitor treated wild-type embryos (C, G, K) and LY411575 inhibitor treated hs:dnfgfr1 embryos (D, H, L). All specimens were treated with 0.3% DMSO and heat-shocked at 24 hpf. The otic vesicle is outlined in each image. (M, N) Mean and standard deviation of the total number of ngn1 positive cells in the otic epithelium at 28 hpf (M) and total neurod positive SAG precursors at 37 hpf (N) for the genotypes and treatments indicated in the color key (counted from serial sections, n = 3–6 ears per time point). Asterisks (*) indicate significant differences from control embryos and filled squares indicate significant differences relative to hs:dnfgfr1 embryos treated with LY411575. (O) Mean and standard deviation of the total number of Isl1 positive SAG neurons at different times for the genotypes and treatments indicated in the color key (n = 6–15 embryos each). In (O) differences between control and experimental specimens were significant at each time point. In addition, LY411575 treated hs:dnfgfr1 embryos were significantly different from hs:dnfgfr1 alone or LY411575 treatment alone.