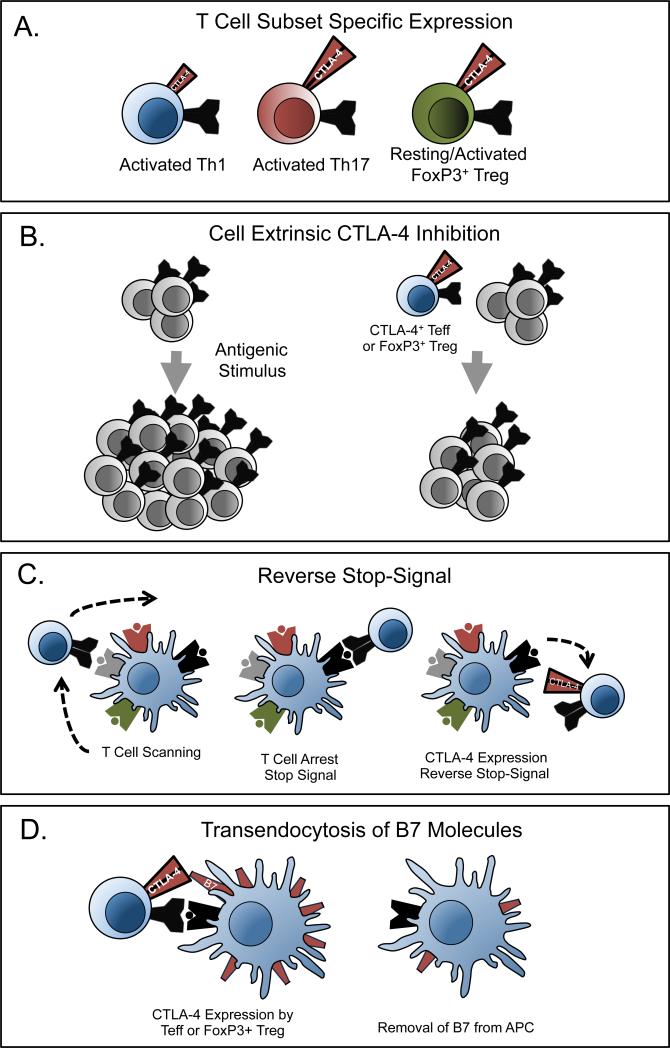
Figure 2. Novel mechanisms of CTLA-4 function.
(A) CTLA-4 expression levels are different on Th1, Th17, and FoxP3+ Treg cells. (B) CTLA-4 expressed on T cells functions in a non-cell autonomous manner to limit the proliferation of other T cells. (C) T cells continuously scan antigen presenting cells for cognate peptide:MHC complexes. Upon binding peptide:MHC binding, T cells arrest this scanning motion, termed a stop signal. The presence of CTLA-4 can block this arrest, termed the reverse stop-signal. (D) CTLA-4 can eliminate the expression of B7 molecules on antigen presenting cells through trans-endocytosis.