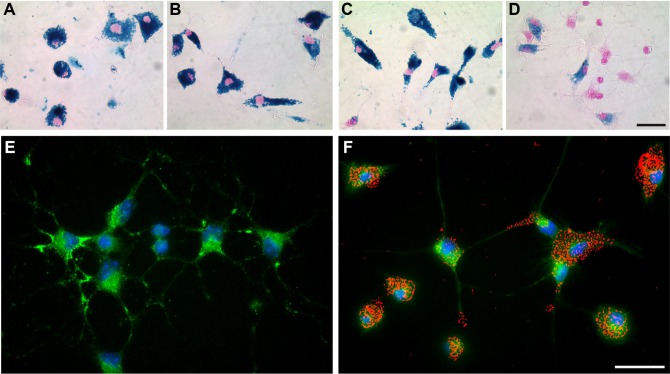
Figure 1.
SPIO accumulation induced alterations of primary microglial morphology.
Notes: Prussian blue staining and nuclear fast red counterstain of microglia exposed to 3.0 mM of VSOP-R1 (A), VSOP-R2 (B), ferucarbotran (C) or ferumoxytol (D) for 24 hours (scale 40 μm). Accumulation of VSOP-R1 (A), VSOP-R2 (B) and ferucarbotran (C) induces activation of microglia that is accompanied by characteristic morphological changes from a ramified toward an amoeboid-like phenotype. Representative images of untreated microglia (E) and microglia incubated for 24 hours with 1.5 mM VSOP-R2 (F) are shown in comparison. Microglia were immunocytochemically stained using green fluorescence CD11b-FITC-conjugated antibody and blue fluorescence nuclear counterstain Hoechst 33258 (scale 20 μm). To visualize cell-associated VSOP-R2, the bright-field image of incubated microglia was captured and pseudocolored in red (F).
Abbreviations: SPIO, superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle; VSOP, very small iron oxide particle; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate.