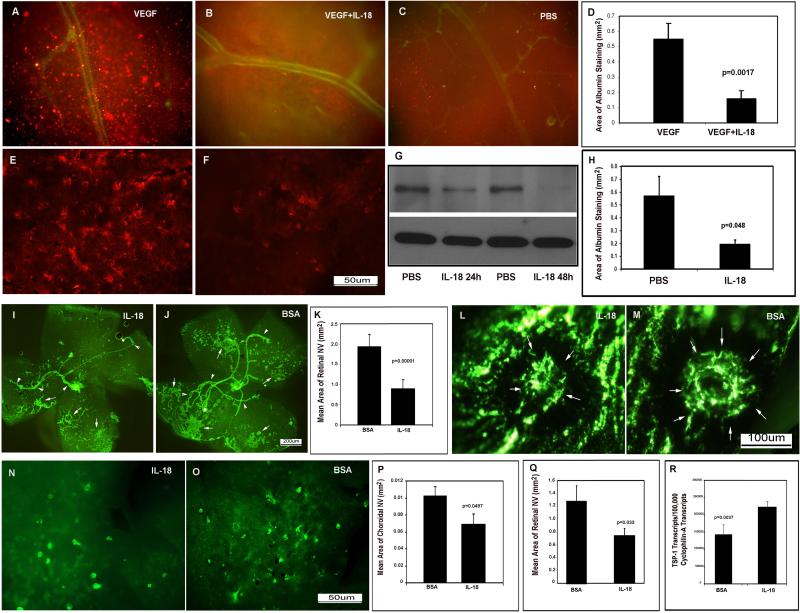
Figure 3. IL-18 prevents VEGF-induced vascular leakage and inhibits retinal and choroidal neovascularization.
Adult C57BL/6 mice were given an intraocular injection of VEGF (A), VEGF + IL-18 (B), or vehicle (C). Equivalent doses of VEGF and IL-18 were given and after 6 hours, mice were perfused with PBS to remove all blood from the vasculature and retinas were stained for albumin (red) and PECAM-1 (green). Retinal flat mounts from eyes injected with VEGF alone (n=8) showed numerous clumps of albumin throughout the retina (A), while those from eyes injected with IL-18 + VEGF (n=7) showed relatively few clumps of albumin (B) and were similar in appearance to retinas from eyes injected with vehicle (C). The mean (±SEM) area of albumin staining per retina was significantly less in eyes injected with IL-18 +VEGF compared with eyes injected with VEGF alone (D). At P21, rho/VEGF mice had injection of IL-18 in one eye and vehicle in the fellow eye and after 24 hours, there was prominent immunoreactive albumin around tufts of NV in vehicle-injected eyes (E), but very little albumin in IL-18-injected eyes (F). Immunoblots for albumin (G, upper panel) showed that 24 or 48 hours after injection of IL-18 there was much less albumin in retinas from IL-18-injected eyes compared to vehicle-injected eye, and reprobing of blots for β-actin demonstrated equal loading (G, lower panel). The area of albumin staining per retina was also significantly reduced 48 hours after injection of IL-18 compared to vehicle-injected fellow eye (H, n=4). At P12, mice with ischemic retinopathy (n=6) were given an intraocular injection of IL-18 in one eye and bovine serum albumin (BSA) in the other eye. At P17, immunostaining for PECAM-1 showed that retinal flat mounts from eyes injected with IL-18 (I) had less NV than those from eyes injected with BSA (J,K). In mice with laser-induced rupture of Bruch's membrane (n=15), eyes injected with IL-18 had significantly less choroidal NV than that seen in eyes injected with BSA (L-M). At P21, eyes of rho/VEGF mice (n=5) that had injection of IL-18 at P14 had less subretinal NV than eyes injected with BSA (N-Q). Mice with ischemic retinopathy were given an intraocular injection of IL-18 at P12 and at P15 total real time RT-PCR showed a significant increase in mRNA for thrombospondin-1 in IL-18-injected eyes compared to BSA-injected eyes (R).