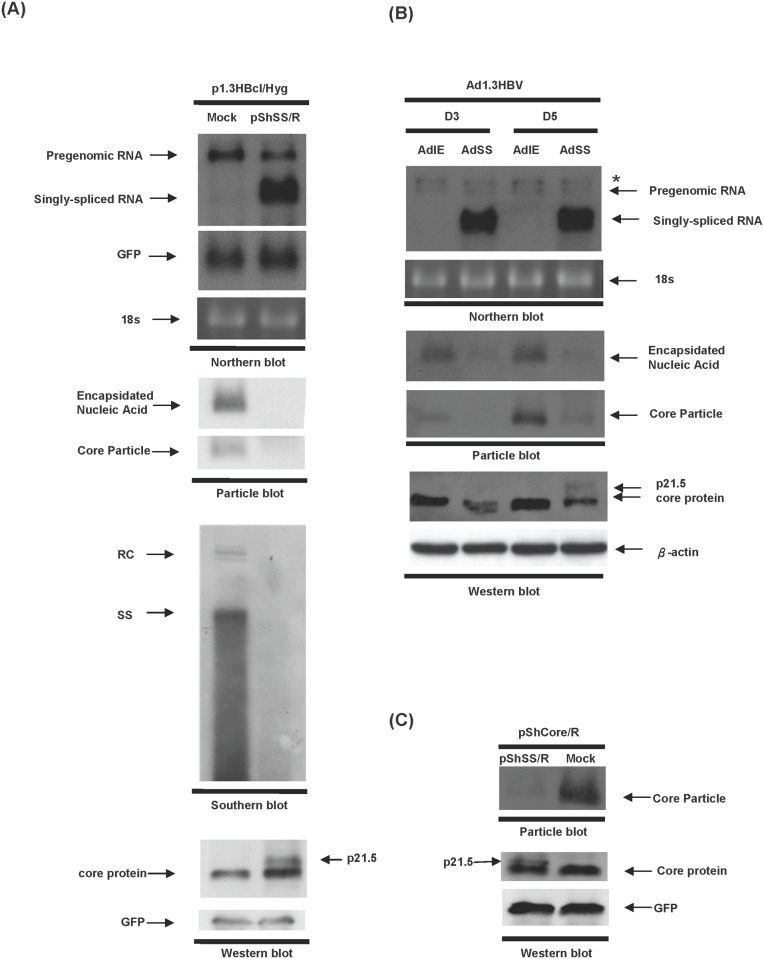
Fig 1. HBV replication is inhibited by overexpression of singly-spliced RNA.
(A) Huh7 cells were co-transfected with p1.3HBcl/Hyg together with either pShSS/R or control plasmid (pShuttle/R, Mock) and the cells were harvested three days post-transfection. Top panel, the expression levels of pgRNA transcript and singly-spliced RNA were revealed by northern blot analysis using hybridization with an HBc-specific probe. The expression level of co-transfected GFP was used as a transfection control and 18s rRNA was used as a loading control. Second panel, the formation of intracellular nucleocapsids was detected by particle blot analysis. Third panel, HBV DNA extracted from intracellular core particles was analyzed by Southern blot analysis. Bottom panel, the expression level of HBV core protein was analyzed by western blot analysis. The expression of GFP protein was used as a loading control. (B) HepG2 cells were co-transduced with Ad1.3HBV together with either AdSS or AdIE for 3 days or 5 days. Total RNA was extracted from the transduced cells and analyzed by northern blot analysis using an HBc-specific probe. The star mark indicates the 3.9 kb X-mRNA generated from the 1.3 copies of the HBV genome of Ad1.3HBV [20]. Total proteins were harvested for particle blot and western blot analyses. The encapsidated nucleic acid was revealed by hybridizing with an HBx-specific probe. The expression level of core protein was detected using anti-core antibody. (C) Huh7 cells were co-transfected with pShCore/R together with either pShSS/R or a control plasmid (Mock), and cell lysate was harvested for particle blot and western blot analyses using anti-core antibody at day 3 post-transfection.