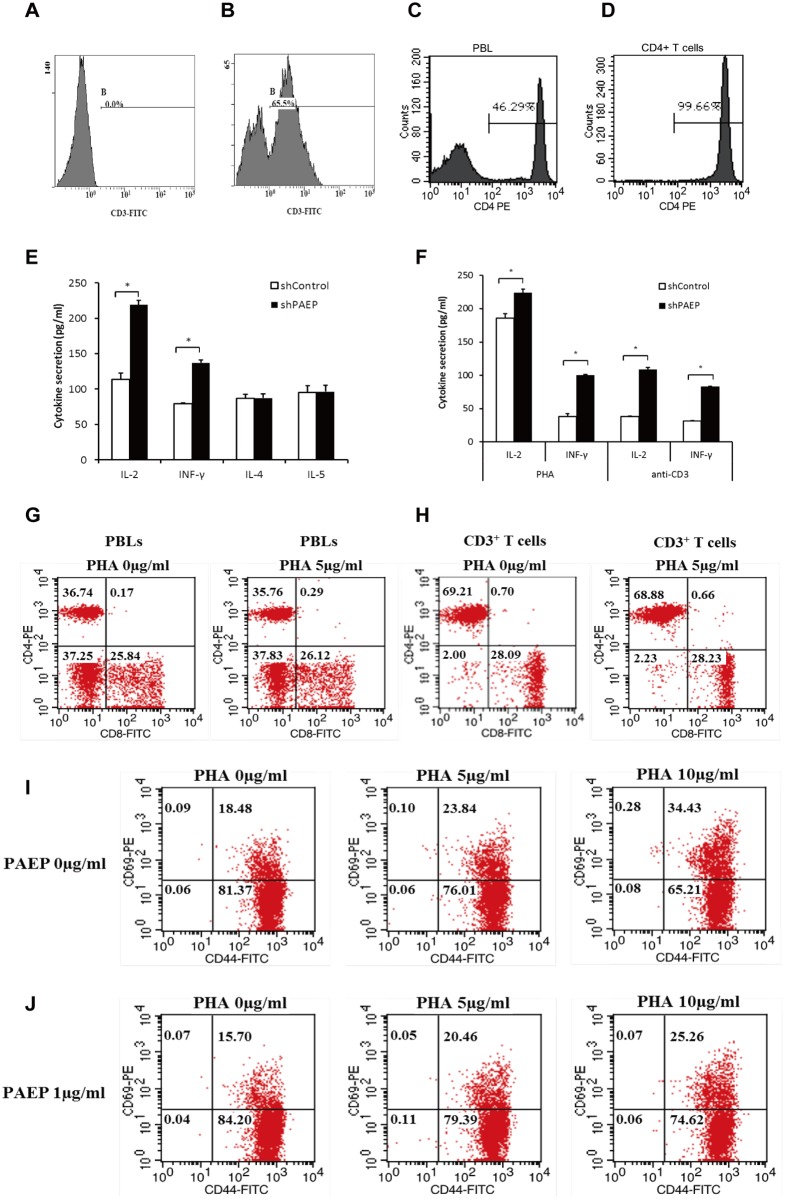
Fig 2. Activation of T helper lymphocytes by melanoma-derived PAEP protein.
(A-B) The percent of CD3+ T cells in unfractionated PBLs from healthy donors was assayed for by direct staining with anti-CD3-FITC followed by flow cytometric analysis. (A) Negative control, (B) Healthy donor. Flow cytometry was applied to confirm the purity of CD4+ T cells before (C) and after (D) MACS isolation. (E) Levels of cytokines secreted by PHA-stimulated T helper cells co-cultured with PAEP-rich 624.38-Mel shControl or PAEP-poor 624.38-Mel shPAEP supernatant were determined. Melanoma-derived PAEP significantly inhibited both IL-2 and IFN- γ secretion by T helper cells (* p<0.05, Student’s t-test). (F) Levels of cytokines secreted by PHA- or anti-CD3 antibody-stimulated Th1 cells co-cultured with PAEP-rich 624.38-Mel shControl or PAEP-poor 624.38-Mel shPAEP supernatant were determined. Melanoma-derived PAEP significantly inhibited both IL-2 and IFN-γ secretion by Th1 cells (* p<0.05, Student’s t-test) (G-H) There were no differences in number of CD4/CD8 cells before or after PHA stimulation in the presence of PAEP (1 μg/ml). (G) PBLs; (H) CD3+ T cells. (I-J) The number of CD69/CD44 cells before and after activation in the absence or presence of PAEP was determined by direct staining with antibodies and flow cytometry. The number of CD69 cells significantly decreased co-cultured with PAEP-rich 624.38-Mel shControl supernatant. The experiment was repeated at least three times.