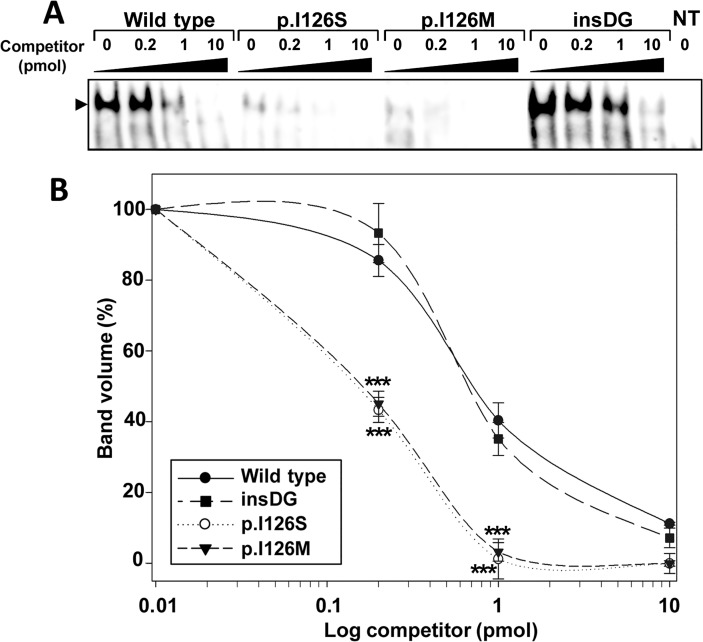
Fig 7. The p.I126S mutation decreases FOXC1 DNA-binding.
(A) The effect of FOXC1 mutations on DNA-binding specificity was assessed via EMSA. The oligonucleotides corresponding to the FOXC1-binding sequence labeled with biotin at the 5'-end were incubated with 10 μg of nuclear extracts from HEK-293T cells transfected with the indicated FOXC1 variants. The extracts were separated on a 10% nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and were transferred to a positively charged nylon membrane (Hybond-N+, Amersham). FOXC1-oligonucleotide complexes were visualized by incubation with streptavidin-HRP conjugate and chemiluminescent detection (Chemiluminescent EMSA kit, Thermo Scientific). Unlabeled competitor oligonucleotides were pre-incubated at increasing concentrations from 0.2 to 10 pmol (1 to 50-fold excess) with the labeled probe. The arrowhead indicates the position of the full-length FOXC1-DNA complexes. (B) The percentage of band volume corresponding to protein-oligonucleotide complexes was estimated by densitometry as indicated in Materials and Methods. Error bars correspond to the SD of three independent experiments carried out in triplicate. insDG: p.G447_G448insDG. NT: non-transfected cells (negative control). Asterisks indicate statistical significance as compared to the control: p<0.001 (***). Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey multiple-comparison test.