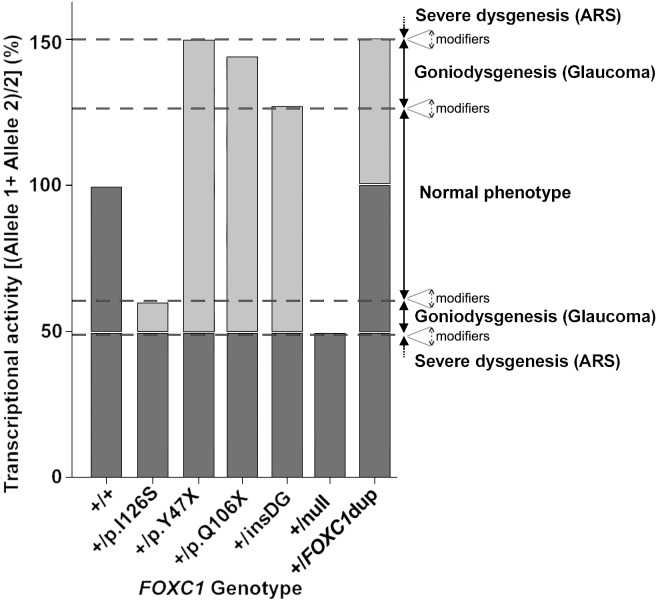
Fig 9. A model for FOXC1 genotype-associated transcriptional activity and phenotypic variability.
The transcriptional activity associated with each FOXC1 genotype is calculated as the mean activity of the two FOXC1 alleles. The model estimates that approximately ±35% activity variations are compatible with a normal ocular development. Mutant genotype activities ranging from approximately 50% to 60% or from 130% to 150% of the wild-type genotype, may lead to moderate goniodysgenesis and dominant glaucoma. Transactivation values equal to 150% [present in heterozygous FOXC1 duplications (+-dupFOXC1)] or lower than 50% [associated with null FOXC1 mutations (+-null) in the heterozygous state] are associated with anterior segment dysgenesis (ASD) and Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome (ARS). The different theoretical thresholds may change by influence of modifier genes and/or environmental factors (dashed arrows). Wild-type and mutant alleles are indicated in dark and light grey, respectively. insDG: p.G447_G448insDG.