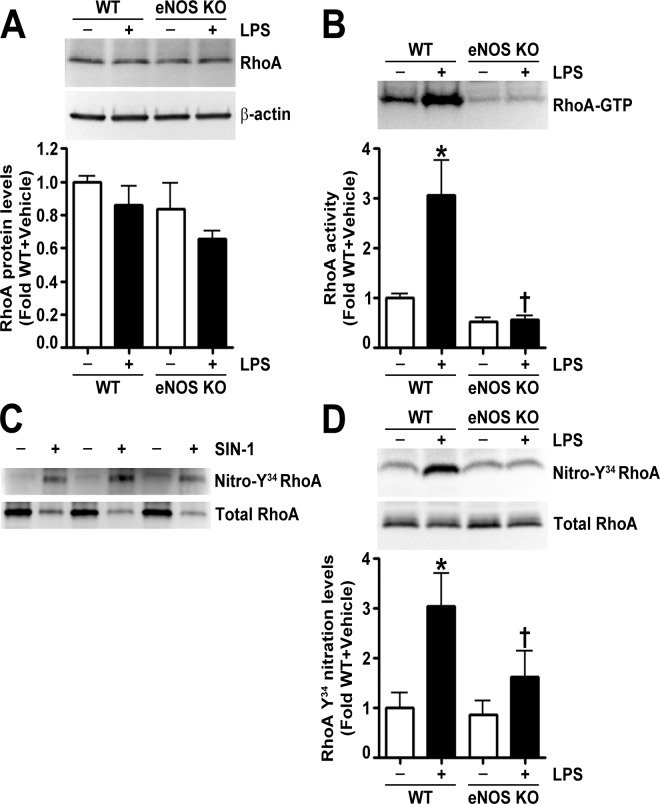
Fig 5. Endothelial NOS deficiency prevents LPS mediated RhoA activation and nitration at Y34 in the mouse lung.
Immunoblot analysis of lung tissue extracts indicated no differences in RhoA protein levels in either wild-type or eNOS-/- mice in the absence or presence of LPS (A). However, LPS induced a significant increase in RhoA activity in the lungs of wild-type mice but not in eNOS-/- mice (B). Recombinant RhoA protein (30 μg) incubated in the presence or absence of SIN-1 (25 mM, 1 h at 37°C) was immunoblotted with an antibody raised against nitro-Y34 RhoA and then normalized with total RhoA antibody. The nitro-Y34 RhoA antibody preferentially bound to nitrated RhoA (C). RhoA Y34 nitration levels in lung extracts were significantly elevated in LPS exposed wild-type mice; however, LPS did not alter RhoA Y34 nitration in the lungs of eNOS-/- mice (D). Values are mean ± SEM, n = 6–10. *p<0.05 vs. Wild-type+Vehicle, †P<0.05 vs. Wild-type+LPS.